![Protecting Sensitive Content Communications Is More Important Than Ever [Kiteworks 2024 Report]](https://www.kiteworks.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Protecting-Sensitive-Content-Communications-Is-More-Important-Than-Ever-Kiteworks-2024-Report-840x390.jpg)
Report: Protecting Sensitive Content Communications Is More Important Than Ever
Another year has passed, and we’re pleased to release our 2024 Kiteworks Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance Report, which provides a deep dive into the critical state of data security and privacy practices across the globe. Drawing from the insights of over 572 IT, cybersecurity, and compliance leaders, our report offers a rich, detailed overview of the challenges and risks that organizations face today in managing their sensitive content. As digital communication and collaboration tools become more integral to business operations, protecting sensitive information has never been more important.
Download an Ungated Copy of the Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance Report Today!
Sensitive content is the lifeblood of any organization—it includes everything from personally identifiable information (PII) and protected health information (PHI) to financial data and intellectual property. A breach or unauthorized access to this information can have devastating consequences, such as financial loss, reputational damage, regulatory penalties, and operational disruptions. Having robust strategies to safeguard this content is essential for maintaining trust and compliance in an increasingly complex threat landscape.
This blog post aims to bring the key findings of the 2024 report to life, highlighting the most pressing security and compliance risks identified by industry leaders. Our goal is to provide you with actionable insights that will help you strengthen your data protection measures, streamline compliance efforts, and effectively manage the risks associated with sensitive content communications. We will explore a variety of topics covered in the report, including security risks, the impact of AI on data protection, compliance challenges, human factors, and best practices for managing sensitive content.
Methodology for the Study
To ensure the 2024 Kiteworks Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance Report provides accurate and relevant insights, a comprehensive survey was conducted. The survey included 33 questions covering various aspects of data security, privacy, and compliance. Conducted by Centiment between February and March 2024, the survey garnered responses from 572 professionals across IT, cybersecurity, and risk and compliance management.
The respondents represented a diverse pool from eight countries globally, including North America, Europe, the Middle East, Africa (EMEA), and the Asia-Pacific regions. These participants came from a wide range of industries, such as security and defense, manufacturing, healthcare, financial services, government, education, and more. The survey cohort included both executive-level professionals (31%) and mid-level management (69%), ensuring a broad perspective on the challenges and priorities in sensitive content protection. This diverse representation provides a robust foundation for the report’s findings and recommendations.
8 Areas of Focus in Data Security and Compliance
In this blog post, I will explore eight critical areas of data security and compliance highlighted in the 2024 Kiteworks Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance Report. Whether you’re an IT professional, a cybersecurity expert, or a compliance manager, this report offers valuable insights and practical advice that can help you navigate the complex landscape of data protection. From understanding the latest security risks and the impact of AI on data protection to addressing regulatory compliance challenges and mitigating human error in breaches, each section is designed to provide you with actionable strategies to protect your sensitive content. Delve into topics such as data breaches, AI-related threats, compliance gaps, and effective risk management to stay ahead in today’s digital age and ensure your organization’s data remains secure and compliant.
1. Security Risks Associated With Sensitive Content
The security of sensitive content is a paramount concern for organizations across all industries. Sensitive content, which includes PII, PHI, financial data, and intellectual property, is a prime target for cybercriminals. The proliferation of digital communication tools and the increased reliance on third-party services have only exacerbated these risks, making it essential for organizations to adopt robust security measures.
Insights From the 2024 Sensitive Content Communications Report
Data breaches continue to be a significant threat to organizations worldwide. According to the 2024 Kiteworks report, nearly one-third of respondents (32%) reported suffering seven or more external malicious hacks of sensitive content in the past year. This represents a slight improvement from the previous year, where 36% of respondents reported similar breaches. However, the frequency of breaches remains alarmingly high across various industries.
Higher education, security and defense, and oil and gas sectors are particularly vulnerable, with 68% or more of respondents in these industries reporting four or more breaches. The federal government sector also revealed concerning data, with 17% indicating they had 10 or more breaches and another 10% reporting between seven to nine breaches. On the other hand, pharmaceuticals and life sciences companies are faring better, with just 28% of respondents reporting four or more breaches.
By understanding these security risks and taking proactive measures, organizations can better protect their sensitive content from unauthorized access and breaches. Implementing advanced security technologies, conducting regular security assessments, and fostering a culture of security awareness are vital steps in safeguarding sensitive information in today’s interconnected digital environment.

2. AI Cyber Risks and Sensitive Content Communications
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries by enhancing efficiency and automating processes. However, its integration into data security systems also introduces new vulnerabilities. AI technologies can both fortify defenses and create avenues for more sophisticated cyber threats. As AI becomes more embedded in business operations, the challenge of safeguarding sensitive content from exploitation increases.
Generative AI (GenAI) and large language models (LLMs) are at the forefront of AI advancements. While these technologies offer substantial benefits, they also pose significant risks. GenAI and LLMs can generate highly realistic text, which cybercriminals can exploit to craft convincing phishing emails, automate social engineering attacks, and create malicious software. The misuse of these technologies by malicious actors presents a serious threat to data security.
Impact of GenAI LLMs and Sensitive Content Communications
One of the primary concerns with GenAI and LLMs is their potential to access and misuse sensitive data. According to Gartner, nearly half of cybersecurity leaders are worried about third-party access to sensitive data through AI tools. Additionally, 40% of respondents express concerns about GenAI application and data breaches, while over one-third fear erroneous decision-making by AI systems. These risks are not hypothetical; they are being realized as employees sometimes input sensitive data into public AI tools without considering the potential security implications.
Insights From the 2024 Sensitive Content Communications Report
The 2024 Kiteworks report sheds light on the growing apprehension surrounding AI-related risks. The survey indicates that organizations are struggling to integrate zero-trust principles effectively, with 48% of respondents finding it challenging to apply these principles across both on-premises and cloud environments. This gap underscores the need for comprehensive security measures tailored to the unique challenges posed by AI technologies.
The report also reveals that 45% of organizations have not yet achieved zero trust with content security, highlighting a significant area for improvement. Certain regions and industries lag in adopting necessary security protocols. For example, only 35% of U.K. respondents and 39% of respondents from the Middle East and Asia-Pacific regions have implemented zero-trust measures for content security. This discrepancy underscores the importance of prioritizing AI security to mitigate potential threats.
Organizations must prioritize securing their AI environments by implementing robust access controls, continuous monitoring, and advanced threat detection mechanisms. Educating employees about the risks associated with AI tools and fostering a culture of security awareness are critical steps in mitigating these risks. By addressing the unique challenges posed by GenAI and LLMs, organizations can better protect their sensitive content and ensure compliance in an AI-driven world.
3. Compliance Risks and Sensitive Content Communications
Navigating the maze of regulatory compliance is one of the most significant challenges facing organizations today. The global landscape of data privacy regulations is becoming increasingly complex, with new laws being introduced and existing ones being updated regularly. Organizations must stay abreast of these changes and ensure their policies and practices comply with a patchwork of regional, national, and international standards. This task is made more difficult by the varying requirements of different jurisdictions, which can lead to significant compliance burdens and increased risk of penalties for noncompliance.
Impact of Global Data Privacy Laws
The impact of global data privacy laws is profound, influencing how organizations manage and protect sensitive content. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has set a high standard for data privacy, prompting other regions to implement similar regulations. In the United States, state-specific laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the more recent California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) add layers of complexity. According to the 2024 Kiteworks report, 93% of organizations have had to rethink their cybersecurity strategies in the past year due to evolving data privacy regulations. This rethinking often involves significant changes to data handling, storage, and sharing practices to ensure compliance.
Compliance is not just about avoiding fines and penalties; it is also about protecting an organization’s reputation and maintaining customer trust. Noncompliance can lead to severe financial and reputational damage, making it essential for organizations to prioritize adherence to data privacy laws.
Insights From the 2024 Sensitive Content Communications Report
The 2024 Kiteworks report reveals several insights into how organizations are managing compliance efforts and where gaps remain. Only 11% of respondents claimed that no improvement was needed in managing compliance risk around sensitive content communication tools. This is a decrease from previous years, indicating a growing awareness of the need for better compliance practices. Conversely, 32% reported that significant improvement is needed, underscoring the ongoing challenges many organizations face.
The report highlights that larger companies are more likely to require significant improvements in their compliance practices. In addition, geographic variations exist, with French respondents showing more confidence in their compliance efforts compared to their counterparts in Germany, the United Kingdom, and the Americas.
One of the most pressing issues identified is the difficulty in tracking, controlling, and reporting on sensitive content sent externally. 43% of organizations admitted to being unable to track, control, and report on all external content exchanges, a substantial governance risk gap. Furthermore, compliance reporting requires considerable staff time, with 62% of respondents spending over 1,500 staff hours annually on this task. This time burden is particularly high for organizations with over 15,000 employees and in sectors like higher education.
Addressing these compliance gaps requires a multi-faceted approach, including investing in advanced tracking and reporting tools, streamlining compliance processes, and fostering a culture of compliance awareness throughout the organization. By taking these steps, organizations can better manage compliance risks and ensure adherence to evolving data privacy regulations.
4. Role of Human Error in Data Breaches
Human error remains one of the most significant risks to data security. Despite advances in technology and automated security measures, the human factor often introduces vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. Employees and third-party partners can inadvertently compromise sensitive content through actions such as misaddressed emails, improper data handling, and falling victim to phishing attacks. The complexity of managing sensitive information across various platforms and communication tools only increases the likelihood of such errors.
Insights From the 2024 Sensitive Content Communications Report
The 2024 Kiteworks report highlights the pervasive impact of human error on data security. According to the report, end-users account for 68% of errors leading to data breaches. This high percentage underscores the critical role that human actions play in compromising sensitive information. The report also notes that industries with higher volumes of sensitive content, such as healthcare and finance, are particularly vulnerable to user-related breaches. In these sectors, the repercussions of a data breach can be especially severe, given the sensitivity of the data involved.
Best Practices to Mitigate Human Risks
To mitigate the risks associated with human error, organizations must implement comprehensive strategies that encompass technology, training, and policy enforcement. Here are some best practices:
- Regular Training and Awareness Programs: Continuous education is crucial. Employees should be trained to recognize phishing attempts, understand data-handling protocols, and stay updated on the latest security threats. Regularly scheduled training sessions and phishing simulations can help reinforce good security habits.
- Implementing Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before accessing sensitive information. This can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access due to stolen or compromised credentials.
- Strict Access Controls: Access controls to sensitive data based on the principle of least privilege ensures that employees only have access to the information necessary for their role. Regular audits can help ensure that access rights are appropriately assigned and maintained.
- Comprehensive Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest can protect information even if it is inadvertently sent to the wrong recipient or accessed by unauthorized individuals.
- Robust Incident Response Plans: Having a clear, well-practiced incident response plan can help organizations quickly contain and mitigate the effects of a data breach. This includes having procedures in place for identifying breaches, notifying affected parties, and complying with regulatory requirements.
By prioritizing these best practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches caused by human error, protecting sensitive content and maintaining compliance with data security regulations.
5. Data Privacy and Compliance and Sensitive Content Communications
Data breaches continue to be a major concern for organizations, with significant implications for privacy and compliance. The 2024 Kiteworks report reveals that nearly one-third of respondents (32%) experienced seven or more external malicious hacks of sensitive content in the past year. Although this represents a slight improvement from the previous year’s 36%, the frequency of breaches remains troublingly high. Higher education, security and defense, and oil and gas sectors are among the most affected, highlighting the need for enhanced protective measures across these industries.
Litigation Costs of Data Breaches
The financial impact of data breaches extends beyond immediate remediation costs. Legal fees associated with data breaches can be substantial, as highlighted in the Kiteworks report. Six in ten respondents reported spending more than $2 million annually on legal costs related to data breaches. For larger organizations, these costs are even higher, with 24% of companies with over 30,001 employees spending more than $7 million annually. Higher education institutions are particularly affected, with 49% reporting litigation costs exceeding $5 million. These figures underscore the importance of investing in robust security measures to prevent breaches and mitigate their financial impact.
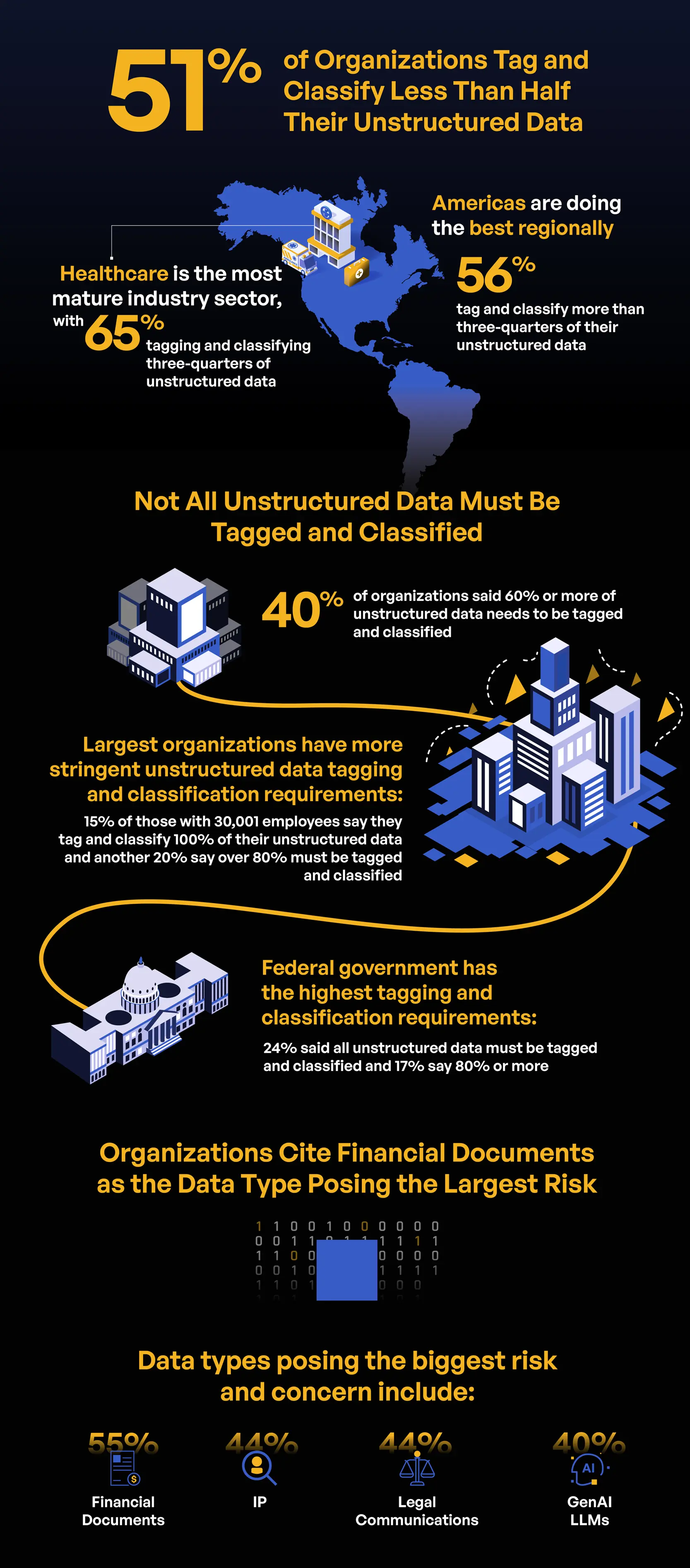
Data Types and Classification Issues
Proper data classification is essential for effective data management and security. The report reveals that many organizations struggle with this fundamental aspect. Less than half of respondents (49%) claim that 75% or more of their unstructured data is tagged or classified. This lack of classification increases the risk of data breaches, as untagged data is harder to track and secure. The healthcare sector performs slightly better, with 66% of organizations achieving this level of data classification, followed by financial services (56%) and legal sectors (55%).
Assessing the Risks of Different Data Types
Different types of data carry varying levels of risk, and organizations must prioritize their protection accordingly. The report indicates that financial documents, intellectual property, and legal communications are the top three concerns for respondents. These data types are critical to the functioning and competitive advantage of organizations, making their protection paramount. Interestingly, while personally identifiable information (PII) is often considered the most sensitive, it was not the top concern for most respondents. This discrepancy suggests a need for organizations to reassess their data protection priorities and ensure that all sensitive data types are adequately safeguarded.
The cross-analysis of data breaches with data types provides further insights. For instance, organizations that prioritized protected health information (PHI) reported higher rates of malicious breaches. This finding aligns with industry trends indicating that healthcare data is a prime target for cybercriminals. Similarly, intellectual property and financial documents are frequently targeted, necessitating robust security measures to protect these high-risk data types.


6. Compliance and Risk Management and Sensitive Content Communications
As organizations grapple with the complexities of data security, compliance and risk management have emerged as top priorities. The ever-evolving landscape of data privacy regulations demands that companies remain vigilant and proactive in their efforts to comply with legal requirements while managing risks effectively. The 2024 Kiteworks report underscores this urgency, revealing that 93% of organizations have had to rethink their cybersecurity strategies in response to new regulations over the past year.
Areas of Focus for Regulations
The global regulatory environment is increasingly stringent, with significant implications for how organizations handle sensitive data. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union remains a benchmark for data privacy, influencing regulations worldwide. In the United States, state-specific laws such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the newer California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) add layers of complexity. The Kiteworks report indicates these regulations are the top focus areas for organizations, with GDPR and U.S. state laws each cited by 41% of respondents. Compliance requires a deep understanding of specific requirements and ongoing adaptation.
Validations and Certifications Prioritized by Organizations
To navigate the compliance landscape effectively, organizations prioritize validations and certifications that demonstrate their commitment to data security. According to the Kiteworks report, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards, particularly ISO 27001, 27017, and 27018, are among the most-cited certifications. Additionally, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 800-171 and the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) are critical, especially for defense sector organizations.
The report highlights that 53% of respondents prioritize ISO standards, while 42% focus on NIST 800-171. This emphasis on recognized standards reflects a trend toward formalizing security practices and meeting global benchmarks. Sectors like pharmaceuticals, healthcare, and financial services are particularly vigilant due to the high stakes associated with data breaches.
Challenges of Data Security Compliance Reporting
Despite best efforts, organizations face significant challenges in compliance reporting. The Kiteworks report reveals that 43% of respondents cannot track, control, and report on all external content exchanges, highlighting a substantial governance risk gap. This difficulty is exacerbated by the complexity of reconciling communication logs across multiple tools.
The time and resources required for compliance reporting are substantial. According to the report, 62% of organizations spend over 1,500 staff hours annually on compliance reporting, with larger organizations facing an even greater burden. Higher education and healthcare sectors are particularly impacted, given the volume and sensitivity of the data they handle. Nearly half of higher education institutions spend over 2,000 hours annually on compliance reporting.
Addressing Compliance Challenges
Organizations must adopt a multi-faceted approach to address these challenges. Investing in advanced tracking and reporting tools, streamlining compliance processes, and fostering a culture of compliance awareness are crucial steps. Implementing automated compliance solutions can significantly reduce the time and effort required for reporting, allowing staff to focus on strategic initiatives.
Regular audits and assessments are essential for identifying gaps and ensuring compliance practices remain effective. By prioritizing continuous improvement and leveraging technology to enhance compliance efforts, organizations can better manage risks and meet evolving data privacy regulations.
7. Cybersecurity and Risk Management and Sensitive Content Communications
The challenge of protecting sensitive content communications is becoming increasingly complex. Organizations use various digital tools and platforms to facilitate communication and data exchange, which unfortunately expands the attack surface for cybercriminals. The 2024 Kiteworks report reveals that many organizations struggle to maintain visibility and control over the flow of sensitive data, leading to increased vulnerabilities. Ensuring the security of sensitive content throughout its life cycle—whether in transit, at rest, or in use—requires comprehensive strategies and continuous vigilance.
Progress Toward Zero Trust
Zero trust is a cybersecurity model that assumes no entity, whether inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. This approach is essential for mitigating risks associated with sensitive content communications. The 2024 Kiteworks report indicates that while progress is being made, significant gaps remain. Approximately 45% of organizations have not yet achieved zero trust for content security. Regions like the U.K., Middle East, and Asia-Pacific are lagging, with only 35% to 39% of respondents reporting the implementation of zero-trust principles.
Advanced Security Measures
Advancing security measures is imperative to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats. Organizations must invest in advanced technologies and practices to bolster their defense mechanisms. Key measures include:
- Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest to ensure it remains secure even if intercepted
- Advanced Threat Detection: Using AI and machine learning to identify and respond to potential threats proactively
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees on the latest security best practices and the importance of safeguarding sensitive information
The 2024 Kiteworks report highlights the need for a proactive approach to security, with 56% of respondents indicating that some improvement in their sensitive content communications security is necessary. This reflects a growing recognition of the importance of continuous improvement and adaptation to new threats.
Tracking and Controlling Sensitive Content Access
Effective tracking and control of sensitive content access are critical components of a robust security strategy. The ability to monitor who accesses sensitive data, when, and how it is used provides invaluable insights for identifying potential security risks. However, only 16% of organizations report being able to track and control access to content consistently.
Key practices for improving content tracking and control include:
- Data Classification: Implementing a robust data classification system to categorize data based on its sensitivity and importance
- Audit Logs: Maintaining comprehensive logs of data access and activity to facilitate audits and investigations
- Automated Alerts: Setting up automated alerts for unauthorized access or unusual activity patterns to enable swift response
Use of Security Tools for Sensitive Content
Deploying a suite of security tools specifically designed for protecting sensitive content is essential. These tools should offer comprehensive capabilities, including encryption, access controls, and monitoring. According to the Kiteworks report, nearly six in ten organizations always use security tools like MFA, encryption, and governance tracking for internal and external communications. However, there is still room for improvement, with many organizations using these tools inconsistently.
Recommended security tools and practices include:
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Enhancing security by requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access to sensitive data
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implementing DLP solutions to detect and prevent unauthorized data transfer
- Integrated Security Platforms: Using integrated platforms, such as security information and event management (SIEM), content disarm and reconstruction (CDR), and others, that provide unified security controls across all communication channels
8. Operational Processes and Sensitive Content Communications
Effective management of operational processes is crucial for mitigating risks associated with sensitive content communications. This section explores key areas where operational challenges and risks intersect, highlighting the need for robust strategies to ensure data security and compliance.
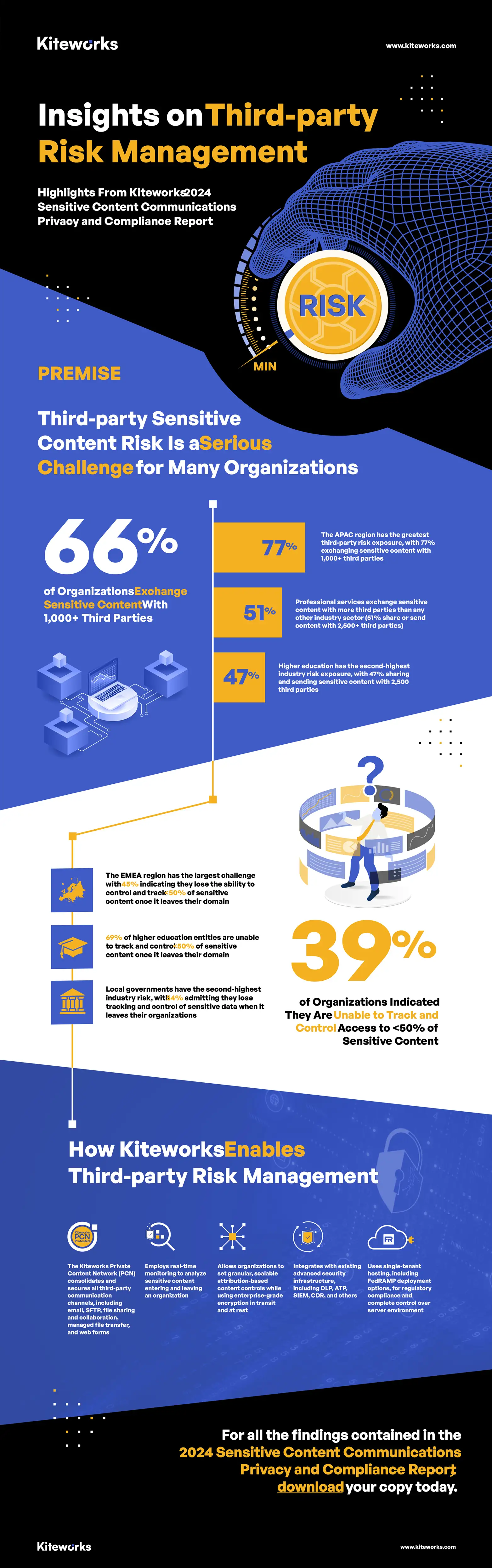
Third-party Multiplication and Risk
As organizations expand their operations, the number of third-party vendors and partners they engage with multiplies, significantly increasing the risk of sensitive content exposure. According to the 2024 Kiteworks report, two-thirds of respondents exchange sensitive content with over 1,000 third parties. Once data leaves the organization, tracking and controlling access becomes more challenging, elevating the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Effective third-party risk management involves rigorous vetting, continuous monitoring, and implementing robust security protocols to ensure that all partners adhere to the organization’s security standards.
Proliferation of Communication Tools and Associated Risks
The proliferation of communication tools—email, file sharing, managed file transfer, and secure file transfer protocols (SFTP)—presents a significant risk to data security. The Kiteworks report highlights that organizations using more than seven communication tools experienced a higher frequency of data breaches. This tool sprawl complicates security management and increases the attack surface for cybercriminals. Consolidating communication tools onto a single platform can reduce complexity, improve security, and enhance operational efficiency.
Log Reconciliation Challenges
Reconciling logs from various communication tools is a time-consuming and complex task, yet it is crucial for compliance and security monitoring. The Kiteworks report reveals that 48% of organizations must reconcile over 11 logs, with 14% needing to consolidate more than 20 logs. This process is particularly burdensome for larger organizations, with those having over 30,001 employees facing significant challenges. Effective log reconciliation requires automated solutions that can aggregate and analyze logs from multiple sources, providing a comprehensive view of data access and activity.
File Size Limits and Associated Risks
File size limits on communication tools often lead to operational inefficiencies and security risks. Employees may resort to using unauthorized, consumer-grade file sharing services to bypass these limits, exposing the organization to potential data breaches. The Kiteworks report indicates that over 30% of organizations need to implement workarounds for file size limits more than 50 times per month across email, file sharing, managed file transfer, and SFTP. Implementing enterprise-grade solutions that support larger file sizes can mitigate these risks and streamline workflows.
Drivers to Address Sensitive Content Communications Risk
The primary drivers for addressing sensitive content communications risks include protecting intellectual property, mitigating litigation, and avoiding regulatory violations. According to the Kiteworks report, 56% of respondents cited the protection of intellectual property and corporate secrets as a top priority. Mitigating litigation costs was identified by 51%, while 48% emphasized avoiding regulatory violations. These drivers highlight the need for comprehensive security strategies that encompass robust data protection measures, compliance with data privacy regulations, and efficient risk management processes.
Effective Strategies for Securing Sensitive Content Communications
The 2024 Kiteworks Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance Report underscores the critical need for organizations to prioritize the protection of sensitive content. The key takeaways from this report highlight the various challenges and risks associated with data security and compliance. From the proliferation of communication tools and third-party risks to the complexities of compliance reporting and the impact of AI on data protection, comprehensive strategies are essential for safeguarding sensitive information.
To address these challenges, organizations should consider the following recommendations:
- Consolidate Communication Tools: Reducing the number of disparate communication tools can significantly lower the risk of data breaches and improve operational efficiency. A single platform for managing sensitive content communications can streamline processes and enhance security.
- Implement Content-defined Zero Trust: Adopting a content-defined zero-trust approach ensures that no entity is trusted by default, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. This involves implementing strict access controls based on the content being accessed, continuous monitoring, and data segmentation.
- Develop Private Content Networks: Establishing private content networks can enhance security by isolating sensitive content communications from public networks. This ensures that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized users within a controlled environment.
- Enhance Security Measures: Invest in advanced security technologies such as encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and advanced threat detection. Regular security awareness training for employees is also crucial to mitigate human error.
- Improve Compliance Reporting: Automate compliance reporting processes to reduce the time and resources required for this task. Ensure that robust tracking and control mechanisms are in place to manage external content exchanges effectively.
- Prioritize Data Classification: Implement a robust data classification system to categorize data based on sensitivity. This helps in identifying high-risk data types and ensuring that appropriate security measures are in place.
Make sure to check out our 2024 report webpage containing numerous content pieces that you can use, such as regional and industry briefs, infographics, the press release, and a Kitecast podcast episode featuring insights from security and compliance leaders. Click here.
FAQs on the 2024 Kiteworks Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance Report
Sensitive content communications are primarily at risk due to data breaches, unauthorized access, and human error. The proliferation of communication tools and third-party engagements further amplifies these risks. Organizations must adopt comprehensive security measures to mitigate these vulnerabilities.
AI technologies, including Generative AI (GenAI) and large language models (LLMs), introduce both opportunities and risks in data security. While they can enhance threat detection, they also create new vulnerabilities for sophisticated cyberattacks. Organizations need robust AI governance to mitigate these risks.
Content-defined zero trust is a security approach that assumes no entity is trusted by default, requiring strict access controls based on the content being accessed. It is crucial for reducing unauthorized access and ensuring sensitive data remains secure. Implementing zero-trust principles helps organizations mitigate potential breaches and enhance overall security.
Organizations can improve compliance reporting by automating processes and implementing robust tracking mechanisms. This reduces the time and resources required for compliance efforts while ensuring accurate and comprehensive reporting. Effective compliance reporting is essential for meeting regulatory requirements and minimizing governance risks.
Consolidating communication tools onto a single platform can significantly lower the risk of data breaches and improve operational efficiency. It reduces complexity, enhances security, and provides better visibility and control over sensitive content communications. This approach simplifies management and strengthens overall data protection strategies.
