What to Expect Ahead of Your CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Audit
CMMC compliance involves undergoing (and passing) a rigorous CMMC compliance audit. In this webinar, a panel of CMMC compliance experts offer best practices for successfully completing the CMMC audit. Recommendations include where to find and how to effectively vet a certified third-party assessor organization (C3PAO), how to develop and use a plan of action and milestones (POA&M), and many other strategies to help defense contractors achieve CMMC compliance.
CMMC Compliance Challenges for Defense Contractors
CMMC compliance requires defense contractors to ensure the security and proper handling of sensitive information like controlled unclassified information (CUI) and federal contract information (FCI). Below are some of the biggest challenges contractors in the defense industrial base (DIB) face when exchanging sensitive data in the context of CMMC compliance.

Secure Email Communications
Email is a common method of communication, but it is also vulnerable to interception and unauthorized access. To mitigate this risk and stay on the right side of CMMC compliance, DIB contractors must implement secure email protocols, such as encryption and digital signatures, to protect and verify the integrity of sensitive information transmitted via email. Additionally, contractors should consider using email solutions that have achieved FedRAMP Moderate authorization, which ensures that the service provider has met stringent security requirements set by the U.S. government.
CUI Identification and Labeling
Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) encompasses a wide range of sensitive information that must be protected, a requirement for CMMC compliance. Defense contractors therefore must develop and implement processes to correctly identify and label CUI across various formats, including digital and physical documents, emails, and digital assets. Properly identifying and labelling CUI facilitates CMMC compliance by ensuring that sensitive information receives the appropriate level of protection and is only shared with authorized individuals.

Access Control and Permission Management
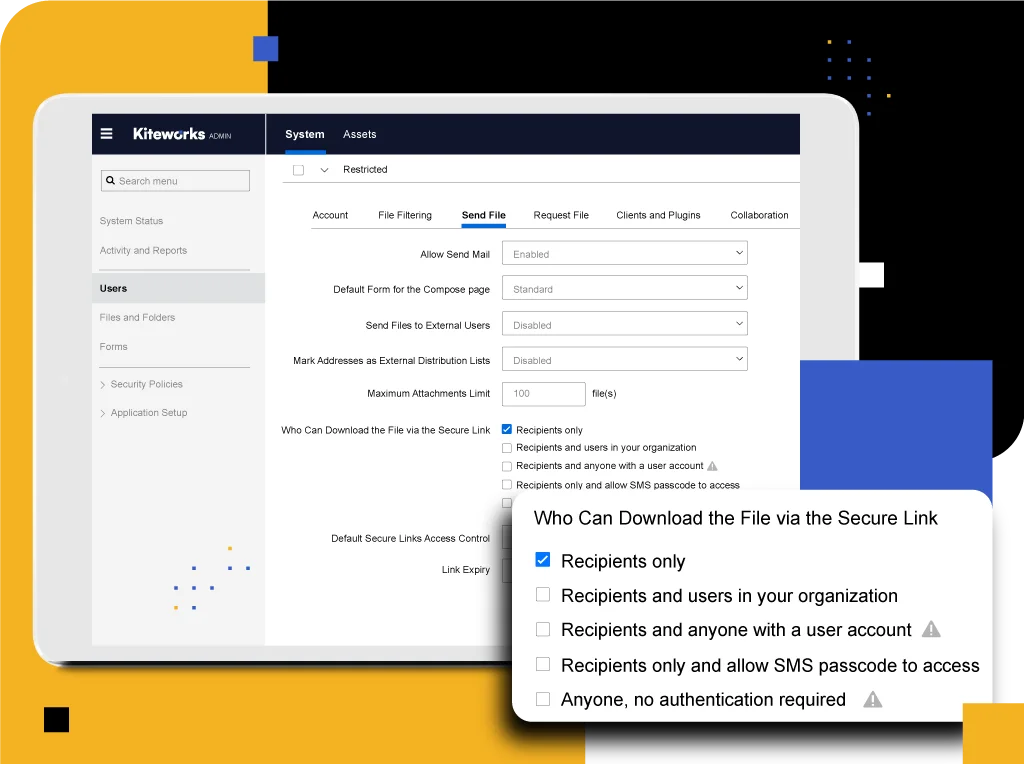
As part of CMMC compliance, DIB contractors must establish strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. This involves implementing role-based access control (RBAC) systems, regularly reviewing and updating user permissions, and promptly revoking access when an employee’s role changes. Contractors must also maintain detailed audit logs that keep a record of access to sensitive data and detect any unauthorized access attempts.
Secure File Sharing and Collaboration
DIB contractors collaborate daily on CUI and FCI with their DoD colleagues. CMMC compliance requires these collaborations to be secure. DIB contractors therefore must use secure file-sharing solutions that provide end-to-end encryption, access controls, and auditing capabilities. When selecting a file-sharing platform, contractors should choose solutions that are FedRAMP authorized for Moderate Impact Level information or higher. This ensures the protections in place adhere to some of the highest levels of security and compliance standards.

Managed File Transfer for Large or Bulk Files
CMMC compliance mandates the secure transfer of large or bulk files containing CUI and FCI between between DIB contractors and their DoD clients. A secure managed file transfer solution should contain features like encryption of data in transit and at rest, access controls, granular permissions, and detailed audit logs. Ideally, managed file transfer solutions should be FedRAMP authorized for Moderate Impact Level information to ensure they meet the highest levels of security and compliance.
Demonstrating Compliance Efficiently
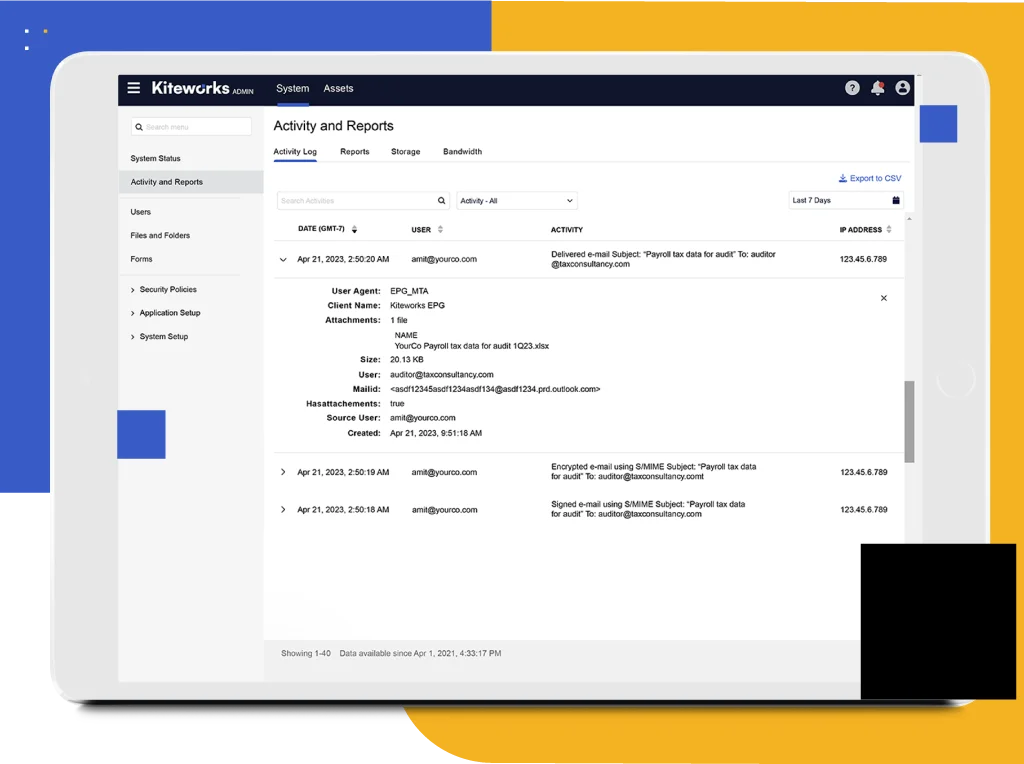
Most communication tools, like email, SFTP, and file-sharing platforms, reside in silos and therefore generate separate audit logs. Aggregating and reconciling these logs as part of a CMMC compliance audit can be, if not virtually impossible, an excruciating and time-consuming task. By contrast, a consolidated, comprehensive audit log that tracks all files containing CUI and FCI that enter and leave the organization can save valuable time and money.

Accelerate Your CMMC 2.0 Compliance Journey With Kiteworks
Control, Protect, and Track Your Sensitive DoD Communications
Demonstrate CMMC compliance whenever you send, share, receive, or store CUI and FCI. Granular access controls, multi-factor authentication, end-to-end encryption, and secure links ensure only authorized users have access to this sensitive data. Consolidate secure email, secure file sharing, secure managed file transfer, secure web forms, and APIs into one platform to unify metadata and standardize security policies and controls. Finally, a single point of integration for security investments like ATP, DLP, CDR, LDAP/AD, and SIEM let defense contractors and subcontractors protect sensitive data for CMMC compliance.
Learn more about Kiteworks security capabilities for protecting FCI and CUI
Fast Track CMMC Compliance With a FedRAMP Deployment
Avoid the time and cost of proving your cloud platform meets 325 NIST 800-53 security controls—critical for CMMC compliance—by adopting one the U.S. federal government has already approved: Kiteworks’ FedRAMP Moderate Authorized Private Data Network. Unlike “FedRAMP equivalent” vendors, Kiteworks undergoes regular pen tests and employee screening, and is backed by strong encryption, physical security, incident response plans, and more. A FedRAMP Moderate Authorization equips defense contractors with genuine evidence of security controls, so they meet a critical CMMC requirement and accelerate CMMC compliance.
Safeguard CUI With Comprehensive Access Controls
Centrally administer a single set of user roles and policies to protect the CUI that flows through all the communication channels the Kiteworks platform consolidates. Mitigate the risk of inadvertent or malicious CUI exposure with default least-privilege access controls over folders, emails, SFTP, managed file transfer flows, and web forms, as well as clients, functions, repositories, and domains. With Kiteworks, administrators apply granular policy controls and role-based permissions for external users to protect CUI from unauthorized access, a critical requirement for CMMC compliance.
Learn more about Kiteworks unified security for protecting sensitive data
Protect CUI With Seamless End-to-End Email Encryption
Safeguard the CUI you share via email with your DoD stakeholders with strong encryption ciphers. Apply your security policies to your email encryption to automate the decision of whether or not to encrypt each email. Automated key exchange ensures user simplicity so your employees work with their normal email standard clients without the need for plugins or training. With end-to-end encryption, you ensure email data and attachments are encrypted from sending client to receiving client while the private decryption key stays in receiving client so neither server-side vendors or attackers can decrypt. Finally, apply your DLP to outbound traffic and your anti-malware and anti-phishing to inbound traffic. You’ll look great in front of your C3PAO and take another step toward CMMC compliance.
Track All File Activity and Simplify Your CMMC Compliance Audit
See who sent CUI or FCI to whom, when, and how so you can track this and other sensitive data entering and leaving your organization, detect suspicious activity, and take action on anomalies. Accelerate CMMC compliance audits with comprehensive, immutable audit logs for all user, automated, and admin activities, including all actions on data, permissions, and configuration. Analyze, alert, and report on the events using built-in tools, or forward to your SIEM via syslog or the Splunk Forwarder for deeper analysis.
Maintain Maximum Security With Tightly Managed Configurations
Adhere to the principle of least functionality required for CMMC compliance by exposing only a few essential ports, with all nonessential services disabled. Protected by a hardened virtual appliance, Kiteworks prevents users and administrators from accessing the operating system or installing software, enforces strict separation of duties, and logs every configuration change. And when you prepare for your CMMC compliance audit, it provides the reporting you need to validate configurations and documented controls.
LEARN MORE ABOUT PROTECTING YOUR SENSITIVE DATA WITH KITEWORKS SECURITY INTEGRATIONS
Enable Productivity Without Compromising Data Custody
Protect CUI and demonstrate CMMC compliance by enabling secure external collaboration on sensitive files without relinquishing control over the original source documents. With Kiteworks SafeEDIT next-generation DRM, CUI and FCI remain safely stored within your environment. By streaming an editable video rendition of files rather than transferring possession, CUI never leaves your security perimeter, providing the highest level of security, control and tracking. Enjoy seamless remote workflows while maintaining strict data protection with a native application experience for editing and collaborating on the streamed file renditions.
LEARN MORE ABOUT PROTECTING SENSITIVE DATA WITH KITEWORKS SAFEEDIT DRM
CMMC Compliance FAQs
CMMC requires end-to-end encryption for all Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and Federal Contract Information (FCI) shared with DoD stakeholders. Defense contractors must use FIPS 140-2 validated encryption for data in transit and at rest, with secure key management protocols. The Kiteworks Private Data Network supports CMMC 2.0 compliance, providing a superior encryption offering: FIPS 140-3 Level 1 validation, as well as automated end-to-end encryption with strong encryption ciphers and seamless key exchange that works with standard email clients without plugins or training required.
CMMC mandates defense contractors develop processes to correctly identify and label CUI across digital documents, emails, and file transfers to ensure appropriate protection levels. Contractors must implement consistent labeling systems and automated detection capabilities across all communication platforms. The Kiteworks Private Data Network consolidates Kiteworks secure email, Kiteworks secure file sharing, secure MFT, and Kiteworks secure web forms into one platform with unified metadata and standardized security policies that automatically apply appropriate CUI protections based on content classification for CMMC 2.0 compliance.
CMMC requires comprehensive, immutable audit logs tracking all CUI and FCI activities including access attempts, file transfers, permission changes, and user actions. Defense contractors must maintain detailed records across all communication channels to demonstrate compliance during assessments. Kiteworks provides consolidated audit logs that track all sensitive data entering and leaving the organization through a single platform, the Private Data Network, eliminating the challenge of reconciling separate logs from siloed communication tools during CMMC audits by C3PAOs for faster CMMC 2.0 compliance.
CMMC mandates role-based access control (RBAC) systems with least-privilege principles, regular permission reviews, and prompt access revocation when roles change. Defense contractors must balance strict security controls with operational efficiency for DoD collaborations. The Kiteworks Private Data Network supports CMMC 2.0 compliance by enabling secure collaboration through centralized user roles and granular policy controls, plus SafeEDIT next-generation DRM that allows possessionless editing of CUI without transferring file possession, maintaining security perimeters while preserving productivity.
CMMC requires secure managed file transfer solutions with encryption for data in transit and at rest, granular access controls, and detailed audit logging for large CUI and FCI files. Defense contractors need FedRAMP Moderate authorized platforms that can handle bulk transfers without compromising security. The Kiteworks Private Data Network provides secure managed file transfer with end-to-end encryption, role-based permissions, and comprehensive audit trails, featuring both a FedRAMP High authorized and FedRAMP Moderate authorized environment that demonstrates FedRAMP compliance and meets CMMC 2.0 compliance requirements for large file exchanges.
FEATURED RESOURCES

Discover How Kiteworks Supports NIST 800-171 Compliance

48 CFR CMMC Proposed Rule Published; Moves CMMC Closer to Implementation

Meeting the FedRAMP Equivalency Requirement of CMMC