
GDPR Compliance: Data Privacy by Design With Encryption and Access
Unless organizations encrypt PII when it’s stored or shared, they jeopardize consumer privacy and risk a data breach or GDPR compliance violation. Kiteworks protects EU consumers’ PII with AES-256-bit encryption for data at rest and TLS 1.2 for data in transit. Advanced encryption features include a FIPS 140-2 Level 1 validated module, and an email protection gateway (EPG) featuring automated, policy-based encryption that protects PII in transit end-to-end. Sole encryption key ownership lets you decide when to rotate so no one, not even Kiteworks, can access your data. Granular access controls set and enforce role-based permissions to limit and restrict access to PII. Require project members or file recipients to verify their identities with multi-factor authentication. Apply your DLP to outbound traffic and your anti-malware and anti-phishing to inbound traffic. SafeVIEW and SafeEDIT DRM innovations enable full dynamic file viewing and editing to ensure that sensitive assets never leave the protected centralized server.
GDPR Compliance: Total Visibility of Every PII Exchange With Comprehensive Reporting
Businesses that have visibility into and control of every file that contains PII have strong data governance, adhere to data privacy standards like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), and more effectively mitigate the risk of a data breach. Kiteworks provides unified visibility of every file containing PII coming into, moving through, and leaving your organization. Monitor and trace all data stored in connected on-premises and cloud ECM systems like OneDrive and Box. All file activity—who shares what with whom, when, and how—is supported by comprehensive reports that allow for file-level analysis. Detailed audit logs capture all file activity and integrate with your SIEM solution, enabling forensic analysis, eDiscovery, and evidence of GDPR compliance. Finally, one-click, audit-ready compliance reports provide detailed visibility into system configurations and security settings, streamlining GDPR audits.
LEARN MORE ABOUT KITEWORKS’ VISIBILITY AND TRACKING CAPABILITIES

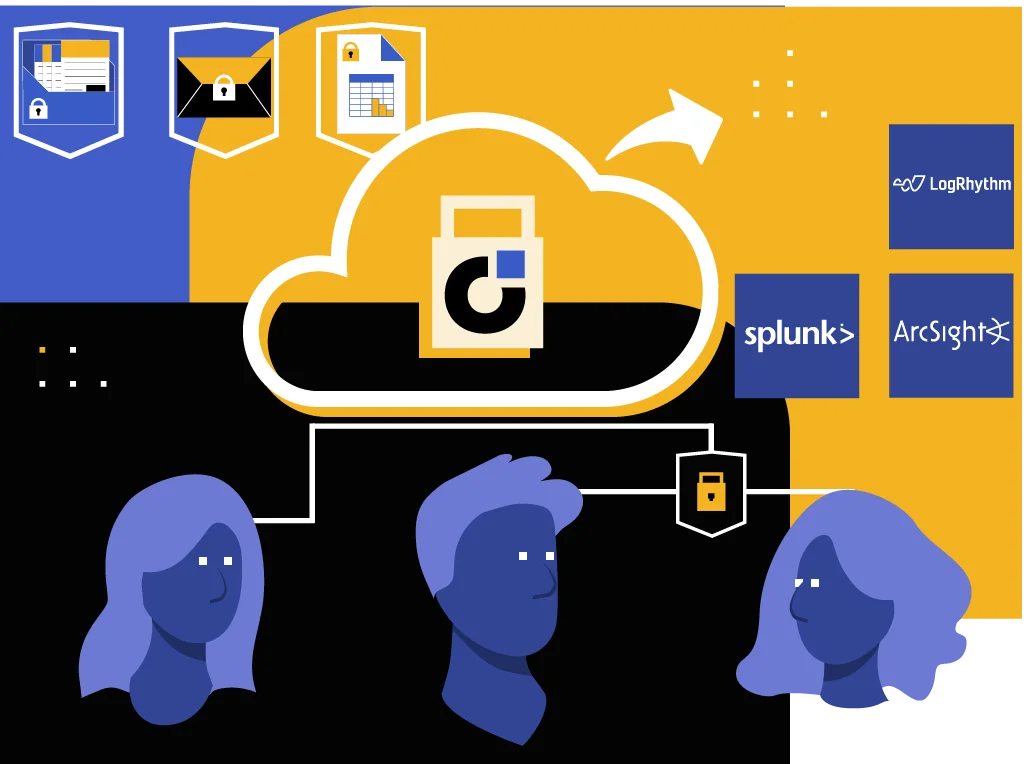
GDPR Compliance: Protect Privacy With Every Email and File Transfer
By sharing PII securely, businesses ensure that EU residents’ rights, such as the right to privacy and data protection, are respected and upheld, in compliance with GDPR. Kiteworks lets you set granular, scalable administrative policies and strict access controls based on role-based permissions, like manager, collaborator, downloader, and view only. Kiteworks also supports file locking, restricting access to a file to one user at a time. Files are protected with AES-256 encryption at rest and TLS 1.2 in transit. In addition, multi-factor authentication prevents unauthorized access to emails and files containing PII. Choose to require MFA for all users, or only for certain users or under certain conditions like users accessing the system from unknown networks. All MFA interactions, just like all file activity, are logged and exportable to a syslog server and read by SIEM products like Splunk, LogRhythm, and ArcSight.
LEARN MORE ABOUT KITEWORKS’ EMAIL AND FILE PRIVACY CAPABILITIES
GDPR Compliance: Comply With Right to Be Forgotten
By complying with the GDPR Right to be Forgotten requirement, businesses demonstrate respect for individuals’ rights to privacy and data protection and avoid public scrutiny, criticism, and potential litigation. Kiteworks helps organizations comply with GDPR’s Right to be Forgotten. Organizations can define data retention policies, specifying how long personal data will be stored and when it will be permanently deleted. Kiteworks provides a centralized platform where all PII is stored, which helps organizations identify all the data they hold about an individual. In the event an individual requests the right to be forgotten, Kiteworks enables organizations to deliver or delete all the relevant data in a single click. All data deletion activities are logged and auditable.
Frequently Asked Questions
GDPR compliance refers to adhering to the regulations set out in the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), a comprehensive data privacy law in the European Union (EU). The GDPR provides guidelines for how EU citizens’ and residents’ personal data must be collected, processed, stored, and shared by organizations, regardless of whether those organizations are based in the EU or elsewhere. To be GDPR compliant, organizations must take steps to ensure that they protect EU citizens’ and residents’ personal data and respect their privacy rights.
The GDPR is based on a set of principles for how personal data should be processed. These principles are intended to ensure that organizations handle EU citizens and residents’ personal data fairly, transparently, and securely.
The three key principles of GDPR compliance are:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: Organizations must process personal data in a lawful, fair, and transparent manner. This includes providing individuals with clear and concise information about how their data will be processed.
- Purpose limitation: Personal data must be collected and processed for specific, explicit, and legitimate purposes. Organizations must not process personal data in a way that is incompatible with these purposes.
- Data minimization: Organizations must collect and process only the personal data that is necessary for the purposes for which it is being processed. They must also ensure that the data is accurate and up to date.
Organizations can ensure GDPR compliance by taking a number of steps to protect EU citizens and residents’ personal data and respect their privacy rights. These steps may include implementing policies and procedures for data protection, appointing a data privacy officer (DPO), and conducting regular data protection impact assessments.
Steps that organizations can take to ensure GDPR compliance include:
- Reviewing and updating data protection policies and procedures to ensure they are aligned with GDPR requirements
- Implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures, such as encryption, access controls, and pseudonymization, to ensure the security of personal data
- Ensuring that individuals have access to their personal data and can exercise their rights under GDPR, such as the right to erasure and the right to object
- Conducting regular audits of data processing activities to ensure compliance with GDPR requirements and to identify areas for improvement
- Ensuring that any third-party processors, such as cloud service providers, are GDPR compliant and have appropriate safeguards in place to protect personal data
- Developing an incident response plan to manage data breaches and unauthorized access to personal data
- Maintaining documentation and records of data processing activities to demonstrate compliance with GDPR requirements
A data protection impact assessment (DPIA) is a process for identifying and assessing the privacy risks associated with a particular data processing activity. A DPIA is required under GDPR for certain types of processing activities that are likely to result in a high risk to EU citizens and residents’ privacy rights.
Yes, U.S. companies need to comply with GDPR if they process personal data of EU citizens and residents. Any company, in fact, regardless of where they are incorporated, must comply with GDPR if they process, hold, or share personal data of EU citizens and residents.
FEATURED RESOURCES

A Quick Guide to the New EU-U.S. Data Privacy Framework

Understanding Data Sovereignty: Regulations, Security, and Compliance in 2023



