
Emerging Trends in Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty is a topic that has garnered increasing attention in recent years due to the rapid digitization of the global economy. As more and more businesses and individuals rely on digital platforms and services, the question of who has control over our data has become paramount.
In this post, we will explore the various emerging trends in data sovereignty, from its definition and importance to the challenges and solutions that accompany it.
What Data Compliance Standards Matter?
Data Sovereignty: a Primer
Data sovereignty refers to the concept that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country in which it is located. It encompasses the idea that data belongs to the individual or organization that generates it, and they have the right to determine how and where it is stored, processed, and shared.
When we talk about data sovereignty, we are essentially discussing the control and ownership we have over our digital footprint. In an increasingly interconnected world, where data is constantly being generated, it is crucial to ensure that our personal and business data is protected from unauthorized access, exploitation, or misuse. Data sovereignty plays a pivotal role in safeguarding sensitive information and protecting national security.
As the value of data continues to rise, both economically and politically, the importance of data sovereignty cannot be overstated. Companies and individuals face the challenges posed by data breaches, data privacy laws, and cross-border data transfers. Understanding data sovereignty is essential for navigating this complex landscape and safeguarding our digital assets.
Definition and Importance of Data Sovereignty
At its core, data sovereignty is about maintaining control and ownership over our digital footprint. It ensures that our personal and business data is protected from unauthorized access, exploitation, or misuse. It also plays a crucial role in protecting national security and safeguarding sensitive information.
Data sovereignty is not just a matter of legal and regulatory compliance; it is also about trust. When individuals and organizations have confidence that their data is being handled in a secure and responsible manner, they are more likely to engage in digital activities and contribute to the growth of the digital economy.
Furthermore, data sovereignty allows individuals and organizations to have a say in how their data is used and shared. It empowers them to make informed decisions about data storage, processing, and transfer, ensuring that their data is handled in a manner that aligns with their values and interests.
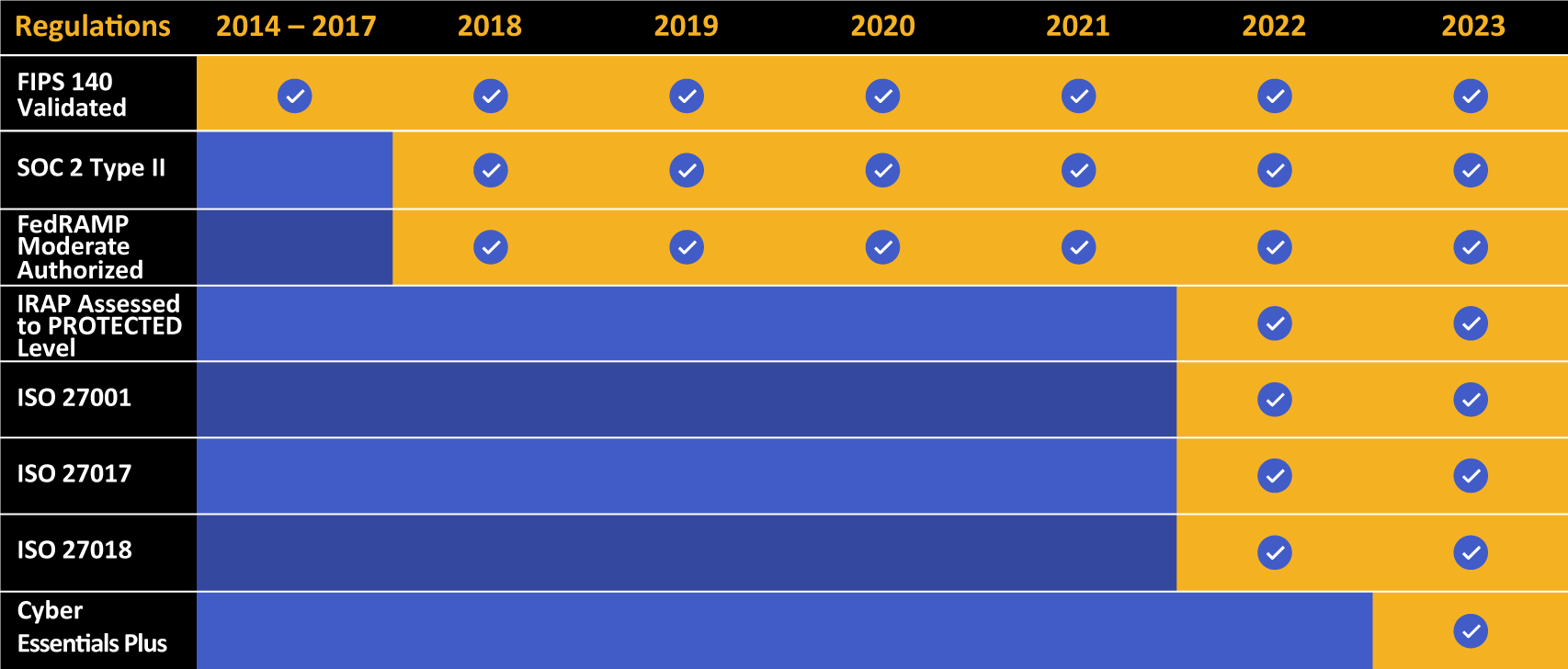
Kiteworks touts a long list of compliance and certification achievements.
The Role of Data Sovereignty in Modern Business
Just as countries vie for control over oil reserves, nations are now competing for data dominance. Data sovereignty allows countries to exercise their regulatory authority and set rules that govern data governance, data protection, and data localization.
By asserting control over their data, countries can drive economic growth, protect national interests, and ensure the security and privacy of their citizens. It also allows policymakers to shape their digital economy and create an enabling environment for innovation and entrepreneurship.
Data sovereignty is not just about protecting national interests; it also has implications for international trade and cooperation. As countries implement data sovereignty measures, they need to strike a balance between protecting their own data and facilitating cross-border data flows. This requires international collaboration and the development of frameworks that promote data protection while fostering global connectivity.
Ultimately, data sovereignty is a complex and evolving concept that requires careful consideration. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, individuals, organizations, and policymakers must work together to ensure that data sovereignty is upheld in a manner that promotes innovation, protects privacy, and fosters trust in the digital age.
The Evolution of Data Sovereignty
To fully appreciate the emerging trends in data sovereignty, it is important to understand its historical evolution. Data sovereignty has its roots in the analog era when countries exercised control over physical assets, such as land, resources, and infrastructure.
In the early days, data sovereignty was a concept that primarily concerned the territorial jurisdiction of physical data storage. Governments asserted their authority over data centers located within their borders, ensuring sensitive information was not vulnerable to foreign interference or surveillance. This approach provided a sense of security, as it allowed countries to maintain control over their data and protect their national interests.
However, as technology advanced and data storage became more decentralized, the concept of data sovereignty needed to adapt. The rise of cloud computing and global data networks posed challenges to traditional notions of territoriality and jurisdiction, giving birth to a new era of data sovereignty.
Historical Perspective of Data Sovereignty
In the pre-digital era, data sovereignty was primarily concerned with the territorial jurisdiction of physical data storage. Governments asserted their authority over data centers located within their borders, ensuring sensitive information was not vulnerable to foreign interference or surveillance.
As the world transitioned into the information age, the volume of data being generated and stored skyrocketed. This exponential growth in data necessitated a shift in how data sovereignty was understood and implemented. It became clear that data sovereignty could no longer be solely based on physical location.
With the advent of the internet, data started flowing across borders at an unprecedented rate. This raised concerns about data security and privacy, as well as the ability of governments to regulate and protect their citizens’ data. The need for a modernized approach to data sovereignty became evident.
Modern Day Data Sovereignty
In the modern digital age, data sovereignty goes beyond physical location. It encompasses legal, technical, and policy considerations surrounding data protection, privacy, and cross-border data transfers. Countries now enact legislation to regulate the collection, processing, and storage of data within their jurisdiction.
This shift in focus has raised important questions about data governance, as the global nature of the internet has made it difficult to enforce national data laws. The tension between sovereignty and globalization is ever-present, as countries seek to strike a balance between protecting their interests and participating in the global digital economy.
Furthermore, data sovereignty is not just a concern for governments. Businesses and individuals also grapple with the challenges it presents. Companies must navigate a complex landscape of data regulations and ensure compliance with multiple jurisdictions. Individuals, on the other hand, are increasingly aware of the importance of data privacy and are demanding greater control over their personal information.
The evolution of data sovereignty has also sparked discussions about the role of international agreements and cooperation. As data knows no borders, finding common ground and establishing frameworks for data governance on a global scale has become a pressing issue. Efforts are being made to develop international standards and protocols that can facilitate secure and responsible data flows while respecting the sovereignty of nations.
Data sovereignty will continue to evolve as technology advances and new challenges emerge. The balance between data protection and the free flow of information will remain a delicate one, requiring ongoing dialogue and collaboration between governments, businesses, and individuals.
Current Trends in Data Sovereignty
The rise of national data laws and the impact of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are two significant trends that shape the current landscape of data sovereignty.
The Rise of National Data Laws
In response to growing concerns over data privacy and security, many countries have enacted their own national data laws. These laws aim to regulate the collection, processing, and storage of data within their jurisdiction, granting individuals greater control and transparency over their personal information.
Examples of national data laws include the European Union’s GDPR, Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (LGPD), and China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL). These laws introduce strict requirements for data protection, impose hefty fines for non-compliance, and require data localization in certain cases.
Impact of GDPR on Data Sovereignty
The introduction of the GDPR in May 2018 has had a profound impact on the concept of data sovereignty. The GDPR establishes stringent rules for data protection, grants individuals expanded rights over their data, and imposes severe penalties for non-compliance.
One of the key provisions of the GDPR is the requirement for data controllers to obtain explicit consent from individuals before processing their personal data. This places the control and ownership of data firmly in the hands of individuals, empowering them to make informed choices about how their data is used.
Furthermore, the GDPR’s extraterritorial effect means that companies outside the European Union must comply with its regulations if they process the data of EU residents. This has prompted many organizations to reassess their data storage and processing practices, leading to a shift towards more localized data infrastructure.
Future Trends in Data Sovereignty
Looking ahead, emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain are set to have a profound impact on data sovereignty.
Predicting the Impact of AI on Data Sovereignty
AI holds immense potential for unlocking value from data. However, AI also introduces new challenges for cybersecurity and data sovereignty. AI systems rely on vast amounts of data to train and make decisions, prompting concerns over data access, ownership, and control.
As AI becomes more prevalent, countries may seek to exert greater control over the data generated within their borders, in an effort to drive economic growth and ensure national security. The development of AI-specific data sovereignty frameworks may become a critical area of focus in the coming years.
The Role of Blockchain in Data Sovereignty
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and transparent nature, has the potential to revolutionize data sovereignty. By leveraging blockchain, individuals and organizations can maintain control over their data through self-sovereign identity and secure, immutable data storage and sharing.
Blockchain-based solutions could enable individuals to selectively disclose their data, granting access to specific entities while maintaining control over the rest. This shift towards user-centric data sovereignty has the potential to empower individuals and foster trust in digital interactions.
Challenges and Solutions in Data Sovereignty
While data sovereignty presents numerous benefits, it also poses challenges that organizations and policymakers must address.
Overcoming Data Localization Challenges
One of the main challenges in data sovereignty is data localization. Some countries require organizations to store and process data within their borders, impeding cross-border data flows and hindering global collaboration.
To overcome these challenges, policymakers and businesses must strike a balance between data protection and the free flow of information. Innovative solutions, such as data protection agreements, cross-border data transfers frameworks, and trusted international data zones, can help reconcile conflicting interests and ensure compliance with national regulations.
Ensuring Compliance in a Global Digital Economy
The global nature of the digital economy presents compliance challenges for organizations operating across borders. Navigating a patchwork of national data laws can be complex and costly, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
To mitigate these challenges, international cooperation and harmonization of data protection regulations are essential. Initiatives such as the APEC Cross-Border Privacy Rules (CBPR) and the Asia-Pacific Privacy Authorities (APPA) strive to promote interoperability and facilitate data transfers while upholding high standards of privacy and security.
Kiteworks Helps Organizations Adhere to Data Sovereignty Requirements
Data sovereignty is a complex and ever-evolving topic. As the world becomes increasingly digitized, understanding the emerging trends and challenges in data sovereignty is crucial for individuals, organizations, and policymakers alike. By grasping the significance of data sovereignty and actively engaging in shaping its future, we can navigate the complexities of the digital era while safeguarding our privacy, security, and economic prosperity.
The Kiteworks Private Content Network, a FIPS 140-2 Level 1 validated secure file sharing and file transfer platform, consolidates email, file sharing, web forms, SFTP and managed file transfer, so organizations control, protect, and track every file as it enters and exits the organization.
Kiteworks plays a crucial role in businesses’ data sovereignty efforts. For example, Kiteworks’ encryption and access control features protect personal information during cross-border transfers, ensuring secure transmission.
Kiteworks’ extensive deployment options, including private, hybrid, and FedRAMP virtual private cloud, can be configured to store data in specific geographic locations. By storing data in specific locations, organizations can ensure that they are adhering to the data sovereignty laws of the countries in which they operate.
Kiteworks also supports data portability requirements by enabling users to securely access, transfer, and download their personal information. Kiteworks also provides organizations with the ability to establish opt-in mechanisms and procedures for data collection, detailed consent forms, and minor consent procedures. These features help organizations comply with consent requirements, which are a key aspect of data sovereignty.
Finally, Kiteworks’ detailed audit trail enables organizations to prove their compliance with data sovereignty laws to auditors.
With Kiteworks: control access to sensitive content; protect it when it’s shared externally using automated end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and security infrastructure integrations; see, track, and report all file activity, namely who sends what to whom, when, and how.
Finally demonstrate compliance with regulations and standards like GDPR, HIPAA, CMMC, Cyber Essentials Plus, IRAP, and many more.
To learn more about Kiteworks, schedule a custom demo today.
Additional Resources
- Brief Expand Visibility and Automate Protection of All Sensitive Email
- Brief Navigate the Digital Trifecta of Data Sovereignty, Cybersecurity, and Compliance With Kiteworks
- Blog Post Data Sovereignty and GDPR [Understanding Data Security]
- Video What Is Email Security? How to Protect Your Sensitive Content With Email Security
- Brief Secure Protocol Package: Strengthening Data Exchange With SFTP and SMTP