Understanding the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act
Data privacy risk has become a critical concern for many states in the U.S. and countries around the world, as the collection, processing, and utilization of personal data have become commonplace. Recognizing the need to protect the privacy and rights of its residents, the state of Texas has taken a significant step toward enacting comprehensive data privacy legislation. The Lone Star State recently passed the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act, joining a growing number of states enacting data privacy laws.

This law aims to establish clear guidelines for businesses operating in Texas and empower Texan residents with greater control over their personal information. Texas’ efforts to enact comprehensive data privacy legislation demonstrate its commitment to safeguarding the privacy and rights of its residents. By taking a proactive approach to data protection, Texas is poised to become a leader in establishing robust privacy regulations that balance the needs of businesses with the interests of consumers.
Let’s delve into the key aspects of the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act, including its applicability, exemptions, consumer rights, sensitive personal information, contract requirements, data assessments, enforcement, and its similarities with other state privacy laws.
Overview of the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act
The Texas Data Privacy and Security Act, often referred to as the TDPSA, is a comprehensive legislation introduced to address concerns regarding data privacy and security within the state of Texas. The Act aims to establish a legal framework for the protection of personal information and ensure that businesses adopt robust data security measures to ensure consumers’ PII is protected and kept private at all times. The TDPSA was introduced in response to the increasing significance of data privacy and security in Texas and the U.S. in general. It recognizes the need to protect individuals’ personal information and establish clear guidelines for businesses operating in Texas.
How the Texas Act Compares and Contrasts With Other State Privacy Laws
The Texas Consumer Data Privacy Act shares similarities with consumer data privacy laws enacted in other states, such as Virginia, Colorado, Utah, Connecticut, and Iowa. These state-level privacy laws reflect a growing concern for protecting consumer rights and personal data in the United States.
While similarities exist, it is important to note that the TDPSA incorporates provisions that are more favorable to small businesses. Small businesses are exempt from the TDPSA unless they engage in the sale of sensitive data, in which case they must obtain explicit consent from consumers.
The TDPSA is modeled after the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) but with a careful combination of measures aimed at striking a balance between consumer protection and the practical considerations of businesses operating within the state. There are other differences, too. In fact, there are two primary differences between these two states’ data privacy acts:
The Definition of Consent: A Difference of Opinion
In both Virginia and Texas, “consent” for consumers is defined as a clear and affirmative action that signifies their voluntary, specific, well-informed, and unambiguous agreement to process personal data concerning them. This definition encompasses a written statement, including an electronically composed statement, or any other unambiguous affirmative action. Texas, however, excludes certain actions, such as accepting a general or broad terms of use document that contains descriptions of personal data processing alongside unrelated information, hovering over, muting, pausing, or closing a given piece of content, or obtaining agreement through the use of dark patterns.
Scope: “Targeted to” vs. “Consumed by”
The VCDPA currently requires entities to either conduct business within the state or target services to its residents to be subject to the law. In Texas, TDPSA replaces the phrase “targeted to” with “consumed by” in order to ensure that compliance with the law is not circumvented.
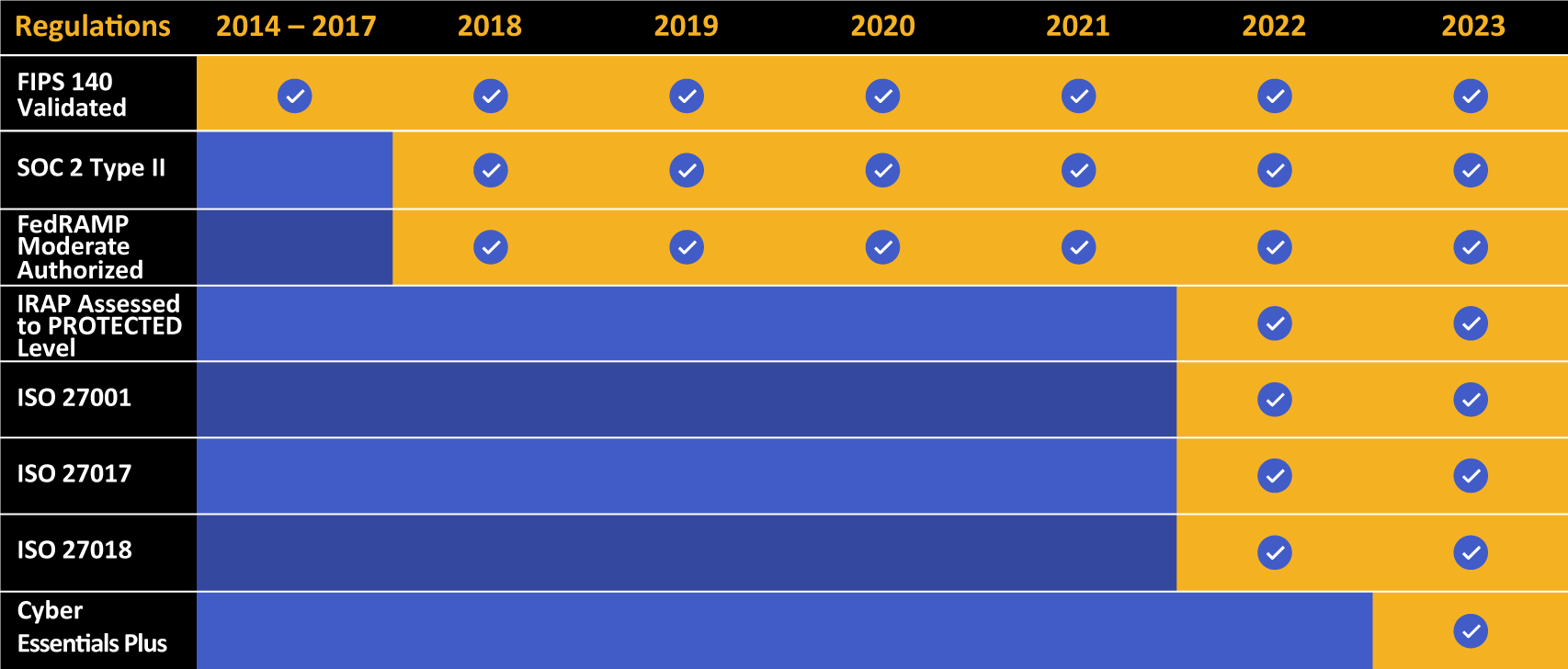
Kiteworks touts a long list of compliance and certification achievements.
Key Provisions of the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act
The TDPSA encompasses various provisions that businesses operating in Texas must comply with to safeguard personal information. Let’s explore some of the essential provisions of the Act:
TDPSA’s Scope and Applicability
The TDPSA applies to businesses operating in Texas or providing products or services to Texas residents. If a business processes or engages in the sale of personal data and is not classified as a small business by the U.S. Small Business Administration, it falls under the purview of the TDPSA. Small businesses, however, are still subject to the TDPSA if they engage in the sale of sensitive content, but only with the prior consent of the consumer. It encompasses both public and private entities, regardless of their size or industry.
TDPSA’s Data Protection Requirements for Businesses
The TDPSA imposes specific obligations on businesses to protect personal information. It requires businesses to implement reasonable security measures to prevent unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of personal data. This includes encryption, access controls, regular risk assessments, and employee training programs.
Consumer Rights and Consent in the TDPSA
The TDPSA emphasizes individuals’ rights concerning their personal information. It grants Texas residents the right to know what personal information is collected, stored, and shared by businesses. It also grants them the right to access their data, request its deletion, request correction of inaccuracies, obtain their data in a portable and readily usable format, and opt out of certain data processing activities. Businesses are required to obtain informed consent from individuals before collecting or using their personal information.
Exemptions Granted by the TDPSA
Certain entities and organizations are exempt from the TDPSA due to existing regulations and laws that govern their data-handling practices. These exemptions include financial institutions covered by the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), entities governed by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, nonprofit organizations, institutions of higher education, and personal information regulated by the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA).
Protecting Sensitive Personal Information Under the TDPSA
The TDPSA places specific emphasis on protecting sensitive personal data, which requires explicit consent from the consumer. Sensitive data includes personal information that reveals racial or ethnic origin, religious beliefs, mental or physical health diagnosis, sexual orientation, citizenship or immigration status, genetic or biometric data used for individual identification, personal data collected from known children, and precise geolocation data.
Contract Requirements Specified in the TDPSA
When a controller (the entity responsible for determining data processing purposes) and a processor (the entity processing data on behalf of the controller) enter into a contract, the TDPSA stipulates specific requirements that must be included. These requirements ensure clarity, transparency, and security in data processing activities. The contract should include instructions for data processing, the purpose and nature of processing, the type of data being processed, the duration of processing, the rights and obligations of both parties, confidentiality obligations, data deletion or return after service completion, availability of information for compliance demonstration, cooperation with assessments, and engagement of subcontractors under similar contractual terms.
Data Assessments in the TDPSA
Controllers are required to conduct and document data protection assessments for specific processing activities. These assessments are essential for evaluating the potential risks associated with data processing. The activities that necessitate data assessments include processing data for targeted advertising, selling personal data, processing data for certain profiling purposes, processing sensitive data, and any processing that poses a heightened risk of harm.
Enforcement of the TDPSA
Under the TDPSA, individuals do not have a private right of action to enforce the provisions of the law. Instead, the responsibility for enforcement lies with the attorney general. If a violation is identified, the attorney general can seek injunctive relief and impose civil penalties on the violating entity. The civil penalty for each violation cannot exceed $7,500. However, the TDPSA allows a grace period of 30 days for a violating party to cure the violation before penalties are imposed.
Furthermore, an additional provision aims to safeguard consumers from discrimination and retaliation when they exercise their rights. If a Texas resident faces any grievances, they have the option to file a complaint with the Texas Attorney General’s office. In the event that a company fails to address the concerns and provide appropriate resolution, the Attorney General’s office has the authority to impose civil fines of up to $7,500 on the offending firm.
Data Protection Requirements for Businesses
The TDPSA imposes explicit obligations on businesses to safeguard personal information. It establishes the need for businesses to implement reasonable security measures that effectively prevent unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of personal PII. The key data protection requirements outlined in the Act include:
Implementation of Reasonable Security Measures
Businesses must adopt and maintain appropriate security measures to protect personal information. This involves implementing safeguards such as encryption, firewalls, and secure authentication protocols to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data.
Access Controls for Data Privacy
Businesses are required to establish access controls that limit data access only to authorized individuals who have a legitimate need for such access. By implementing access controls, typically by role-based permissions, businesses can minimize the risk of unauthorized disclosure or misuse of personal information.
Regular Risk Assessments to Mitigate Vulnerabilities
The TDPSA emphasizes the importance of conducting regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats to PII. By evaluating risks, businesses can proactively implement measures to mitigate vulnerabilities and enhance their overall data security posture.
Incident Response and Breach Notification
The TDPSA requires businesses to establish incident response plans to effectively address and manage data breaches or security incidents. Additionally, businesses must promptly notify affected individuals and, in certain cases, regulatory authorities in the event of a data breach as per the breach notification requirements outlined in the Act.
Privacy Policies and Disclosures for Full Transparency
Businesses must develop and maintain clear and transparent privacy policies that outline how personal information is collected, used, shared, and protected. These policies should be easily accessible to individuals and provide concise information about the business’s data-handling practices.
Vendor and Third-party Management for Data Protection
The Act emphasizes the importance of businesses ensuring that their vendors and third-party service providers also adhere to appropriate data protection practices. Businesses should implement robust contracts and agreements that include data protection obligations for their vendors and third-party partners.
By adhering to these data protection requirements, businesses can effectively safeguard Texans’ personal information, minimize the risk of data breaches, and demonstrate compliance with the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act.
TDPSA Implications for Businesses
The Texas Data Privacy and Security Act carries significant implications for businesses operating within the state. These implications include:
- Enhanced Data Protection Obligations: The Act mandates businesses to implement robust data protection measures, such as encryption and access controls, to ensure the security and confidentiality of personal data. This necessitates a comprehensive review and potential restructuring of existing data-handling practices.
- Compliance Costs: Businesses must allocate resources and invest in technologies, personnel, and training to comply with the Act’s requirements. Implementing data privacy measures, conducting privacy assessments, and training employees on data-handling best practices may incur additional expenses.
- Consumer Trust and Reputation: Demonstrating compliance with the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act can enhance consumer trust and bolster a company’s reputation. By prioritizing data privacy and security, businesses can differentiate themselves and attract customers who value their personal information protection.
- Legal and Regulatory Risks: Noncompliance can lead to severe legal and financial repercussions. Businesses failing to meet the data protection obligations may face penalties, fines, legal disputes, and potential reputational damage. Adhering to the TDPSA’s provisions is crucial to mitigating legal and regulatory risks.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that proactively implement strong data privacy and security measures gain a competitive edge. Demonstrating a commitment to protecting consumer data can attract privacy-conscious customers and position the business as a trusted entity in the marketplace.
- Data Governance and Accountability: The TDPSA necessitates robust data governance practices, including clear policies, procedures, and documentation surrounding data handling and protection. Implementing accountability measures ensures transparency, traceability, and compliance with the Act’s provisions.
- Business Partnerships and Contracts: Businesses operating in Texas may need to review and update contracts with vendors, partners, and service providers to ensure alignment with the TDPSA’s requirements. This may include incorporating data protection clauses, liability provisions, and compliance commitments into contractual agreements.
- Educating Employees and Staff: Training and educating employees about data privacy and security practices become paramount. By raising awareness and promoting a culture of privacy within the organization, businesses can minimize the risk of data breaches and enhance overall compliance.
Kiteworks Helps Businesses Comply With the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act
Once the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act becomes effective on March 1, 2024, private and public entities operating in Texas and those whose services are consumed by Texas residents must comply with the Act to avoid legal and financial repercussions as well as reputational damage.
In order to comply with the TDPSA, businesses must take steps to properly track, control, and secure the digital communications of personally identifiable information (PII) belonging to Texas residents.
By consolidating communication channels into a Private Content Network, Kiteworks enables organizations to demonstrate compliance with the TDPSA and many other state, regional, and industry data privacy regulations while unifying, tracking, controlling, and securing PII. Whether businesses use email, file sharing, managed file transfer, web forms, or other channels to exchange PII with trusted partners, files are protected with access controls, multi-factor authentication, and TLS 1.2 encryption in transit and AES-256 encryption at rest.
Schedule a custom demo to learn how Kiteworks’ platform can help your organization securely share and store PII in compliance with the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act.

