
5 Steps to Data Sovereignty Success
Data sovereignty has become a critical concern for organizations across various industries. The ability to maintain control over your data and ensure compliance with local regulations is crucial for businesses operating in a global marketplace.
To achieve data sovereignty success, organizations need to understand the concept, assess their current data landscape, develop a comprehensive strategy, implement effective measures, and continuously monitor and maintain their data sovereignty practices.
What Data Compliance Standards Matter?
Step 1: Understand Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty refers to the concept of maintaining control over your data and ensuring it is subject to the laws and regulations of the jurisdiction in which it resides. In a world where data flows across borders and through cloud services, organizations need to be aware of where their data is located and who has access to it. Data sovereignty is not only about compliance; it also encompasses data security, privacy, and protection.
Data sovereignty has become increasingly important in today’s digital landscape. With the rapid growth of data-driven technologies and the increasing reliance on cloud services, organizations face new challenges in protecting their data. The ability to maintain control over data, regardless of its location, is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance with local regulations and to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
The Importance of Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it helps organizations comply with local regulations regarding data protection and privacy. Different countries have different laws and regulations governing the handling of data, and organizations must ensure that their data practices align with these requirements. By maintaining data sovereignty, organizations can avoid legal complications and potential penalties associated with non-compliance.
Secondly, data sovereignty enables businesses to mitigate risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access. By knowing where their data is located and who has access to it, organizations can implement appropriate security measures to protect against potential threats. This includes implementing robust encryption protocols, access controls, and monitoring systems to detect and respond to any suspicious activities.
Finally, data sovereignty builds trust with customers and partners. In an era where data breaches and privacy concerns are prevalent, customers and partners are increasingly cautious about sharing their data. By demonstrating a commitment to data sovereignty, organizations can assure their stakeholders that they take data privacy and security seriously. This can enhance their reputation, attract new customers, and foster stronger relationships with partners.
Key Principles of Data Sovereignty
There are several key principles that organizations should consider in their efforts to achieve data sovereignty. Firstly, they need to be aware of the geographical location of their data. This includes understanding where their data is stored, whether it is in physical data centers or in the cloud. By knowing the location of their data, organizations can assess the legal and regulatory requirements that apply to it.
Secondly, organizations must ensure that their data storage and processing arrangements align with local regulations. This involves understanding the specific data protection and privacy laws of the jurisdictions in which their data resides. It may require implementing additional security measures, such as data encryption or data residency requirements, to comply with these regulations.
Thirdly, organizations should implement data access and control mechanisms that safeguard their data. This includes implementing strong authentication and authorization protocols to ensure that only authorized individuals can access and manipulate the data. It also involves regularly reviewing and updating access permissions to reflect changes in roles and responsibilities within the organization.
Furthermore, organizations should consider implementing data backup and disaster recovery plans to ensure the availability and integrity of their data. This includes regular backups, offsite storage, and testing of recovery procedures to minimize the impact of potential data loss or system failures.
In conclusion, data sovereignty is a critical aspect of data management in today’s interconnected world. By understanding the importance of data sovereignty and implementing the key principles, organizations can protect their data, comply with regulations, and build trust with their stakeholders.
Step 2: Assess Your Current Data Landscape
Before embarking on the journey to data sovereignty, organizations need to have a clear understanding of their current data landscape. This involves identifying the types of data they collect, where it is located, and the data management practices in place.
When it comes to data collection, organizations need to be aware of the various types of data they collect and process. This could include personal data, such as names, addresses, and contact information, as well as financial information, proprietary business data, and more. By conducting a comprehensive data audit, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the data they possess and its potential value.
Simultaneously, organizations need to determine the geographical locations where this data is stored or processed. With the increasing use of cloud computing and outsourcing, data can be spread across multiple servers and data centers located in different countries. Understanding the physical locations of data is crucial for ensuring compliance with data sovereignty regulations and for assessing potential risks associated with data storage and processing.
Identifying Data Types and Locations
Organizations should conduct a comprehensive data audit to identify the types of data they collect and process. This could include personal data, financial information, proprietary business data, and more. By conducting a thorough analysis, organizations can gain insights into the nature of their data and its potential vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, it is important for organizations to consider the sensitivity of the data they possess. Some data may be more sensitive than others, requiring additional security measures and stricter data sovereignty protocols. By categorizing data based on its sensitivity, organizations can prioritize their efforts and allocate resources accordingly.
Once the types of data have been identified, organizations need to determine the geographical locations where this data is stored or processed. This is particularly important in the context of data sovereignty, as different countries have different laws and regulations governing the storage and processing of data. By understanding the physical locations of data, organizations can ensure compliance with relevant regulations and mitigate potential risks associated with data storage and processing.
Evaluating Current Data Management Practices
Assessing the effectiveness of current data management practices is equally crucial. Organizations should evaluate their data governance policies, data access controls, encryption mechanisms, and data protection measures. By conducting a thorough evaluation, organizations can identify any gaps or vulnerabilities in their existing practices and take targeted actions to improve their data sovereignty.
Data governance policies play a critical role in ensuring the appropriate handling and protection of data. Organizations should assess the comprehensiveness and effectiveness of their policies, ensuring that they align with industry best practices and regulatory requirements. This includes establishing clear guidelines for data collection, storage, access, and sharing, as well as defining roles and responsibilities for data management within the organization.
Data access controls are another important aspect of data management. Organizations should evaluate the mechanisms in place to control access to data, ensuring that only authorized individuals have the necessary permissions to view, modify, or delete data. This includes implementing strong authentication measures, such as multi-factor authentication, and regularly reviewing access privileges to prevent unauthorized access.
Encryption is a key component of data protection. Organizations should assess the encryption mechanisms they have in place to safeguard data both at rest and in transit. This includes evaluating the strength of encryption algorithms used, ensuring that encryption keys are properly managed, and implementing mechanisms to detect and respond to any potential breaches in encryption.
Lastly, organizations should evaluate their data protection measures, such as backup and disaster recovery plans. It is important to assess the effectiveness of these measures in ensuring data availability and integrity, as well as their ability to recover from potential data breaches or system failures.
By evaluating their current data management practices and identifying any gaps or vulnerabilities, organizations can take targeted actions to improve their data sovereignty. This includes implementing stronger data governance policies, enhancing data access controls, strengthening encryption mechanisms, and improving data protection measures overall.
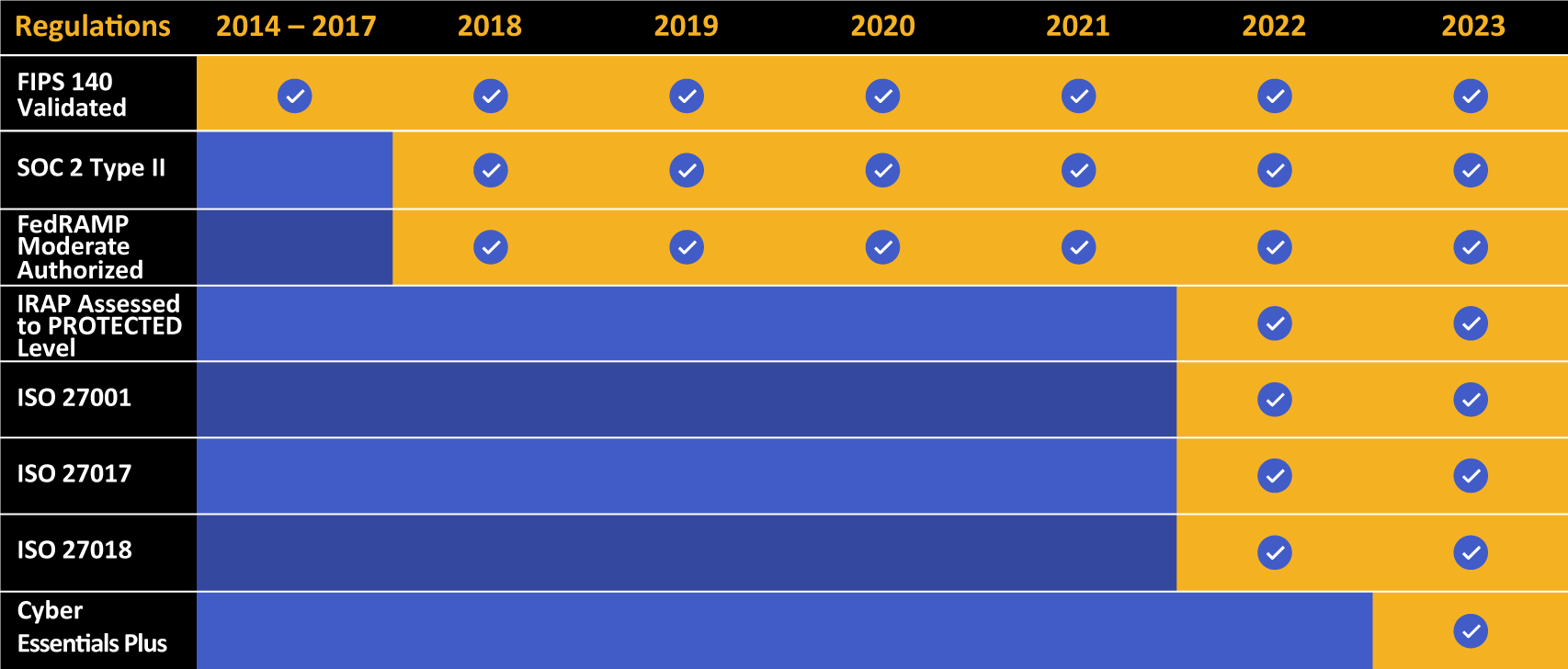
Kiteworks touts a long list of compliance and certification achievements.
Step 3: Develop a Data Sovereignty Strategy
Once organizations have a clear understanding of their current data landscape, they can develop a comprehensive data sovereignty strategy.
Developing a data sovereignty strategy involves more than just understanding the current data landscape. It requires organizations to delve deeper into their data governance practices and align them with their overall business objectives. This process involves identifying key stakeholders, such as legal and compliance teams, IT departments, and business leaders, to ensure that all perspectives are considered.
Setting Data Sovereignty Goals
Organizations should set clear goals for their data sovereignty initiatives. These goals should be aligned with the organization’s overall vision and mission. For example, a financial institution may prioritize compliance with local data protection laws to protect customer information, while a technology company may focus on enhancing customer trust by implementing stringent data security measures.
By setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals, organizations can track their progress and evaluate the success of their data sovereignty efforts. These goals should be communicated across the organization to ensure that everyone is working towards a common objective.
Planning for Data Compliance and Security
Developing a robust data compliance and security plan is essential for organizations aiming to achieve data sovereignty success. This involves more than just identifying potential risks and implementing safeguards. It requires organizations to conduct a thorough assessment of their data flows, both internally and externally.
Mapping data flows involves understanding how data is collected, stored, processed, and transmitted within the organization. It also involves identifying any third-party vendors or partners who have access to the organization’s data. By having a clear picture of data flows, organizations can identify potential vulnerabilities and implement appropriate controls to mitigate risks.
In addition to mapping data flows, organizations should also establish data breach response procedures and protocols. These protocols should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident, including notifying affected parties, conducting forensic investigations, and implementing remediation measures. By having a well-defined response plan, organizations can minimize the impact of security incidents and maintain customer trust.
Furthermore, organizations should regularly review and update their data compliance and security plan to adapt to changing regulatory requirements and emerging threats. This includes staying up to date with new data protection laws and industry best practices.
In conclusion, developing a data sovereignty strategy requires organizations to set clear goals, plan for data compliance and security, and continuously review and update their practices. By taking a proactive approach to data governance, organizations can ensure the protection of their data, enhance customer trust, and achieve operational efficiency.
Step 4: Implement Data Sovereignty Measures
With a well-defined strategy in place, organizations can move on to implementing effective measures to achieve data sovereignty.
Data Localization and Storage Solutions
One of the critical aspects of data sovereignty is ensuring that data remains within a specific geographic jurisdiction. Organizations should consider localizing their data storage and processing to comply with local regulations. This may involve establishing on-premises data centers or partnering with cloud service providers that offer localized data storage solutions.
Data Access and Control Mechanisms
Implementing robust data access and control mechanisms is crucial for data sovereignty. This includes defining access privileges, enforcing strong authentication and authorization mechanisms, and monitoring data access activities. By adopting a least privilege principle, organizations can control who can access and modify their data, reducing the risk of unauthorized data exposure or tampering.
Step 5: Monitor and Maintain Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and maintenance.
Conduct Regular Data Audits
Organizations should conduct regular data audits to ensure ongoing compliance with local regulations and internal data governance policies. These audits help identify any deviations from established practices and enable timely corrective actions. By regularly reviewing and updating data mapping and control mechanisms, organizations can adapt to changing regulatory requirements and emerging data risks.
Update Data Sovereignty Measures
Data sovereignty is not a one-time implementation; it requires organizations to keep up with evolving technologies, regulations, and industry best practices. Regularly reviewing and updating data sovereignty measures ensures that organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and potential vulnerabilities.
Kiteworks Helps Organizations Achieve Data Sovereignty with a Private Content Network
Achieving data sovereignty success involves a series of steps starting from understanding the concept to implementing effective measures and continuously monitoring and maintaining data sovereignty practices. By prioritizing data sovereignty, organizations can protect their data, comply with local regulations, and build trust with customers and partners. Data sovereignty is not just a legal requirement but a strategic investment in the long-term success and sustainability of an organization’s data management practices.
The Kiteworks Private Content Network, a FIPS 140-2 Level 1 validated secure file sharing and file transfer platform, consolidates email, file sharing, web forms, SFTP and managed file transfer, so organizations control, protect, and track every file as it enters and exits the organization.
Kiteworks plays a crucial role in businesses’ data sovereignty efforts. For example, Kiteworks’ encryption and access control features protect personal information during cross-border transfers, ensuring secure transmission.
Kiteworks’ extensive deployment options, including private, hybrid, and FedRAMP virtual private cloud, can be configured to store data in specific geographic locations. By storing data in specific locations, organizations can ensure that they are adhering to the data sovereignty laws of the countries in which they operate.
Kiteworks also supports data portability requirements by enabling users to securely access, transfer, and download their personal information. Kiteworks also provides organizations with the ability to establish opt-in mechanisms and procedures for data collection, detailed consent forms, and minor consent procedures. These features help organizations comply with consent requirements, which are a key aspect of data sovereignty.
Finally, Kiteworks’ detailed audit trail enables organizations to prove their compliance with data sovereignty laws to auditors.
With Kiteworks: control access to sensitive content; protect it when it’s shared externally using automated end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and security infrastructure integrations; see, track, and report all file activity, namely who sends what to whom, when, and how.
Finally demonstrate compliance with regulations and standards like GDPR, HIPAA, CMMC, Cyber Essentials Plus, IRAP, and many more.
To learn more about Kiteworks, schedule a custom demo today.
Additional Resources
- Brief Expand Visibility and Automate Protection of All Sensitive Email
- Brief Navigate the Digital Trifecta of Data Sovereignty, Cybersecurity, and Compliance With Kiteworks
- Blog Post Data Sovereignty and GDPR [Understanding Data Security]
- Video What Is Email Security? How to Protect Your Sensitive Content With Email Security
- Brief Secure Protocol Package: Strengthening Data Exchange With SFTP and SMTP
