
115 Top Cybersecurity Stats in 2023
Keeping sensitive content secure and organizations and systems compliant with data privacy regulations and standards is critical for today’s business. Digital transformation now extends to all industry segments and organizations of virtually any size. The volume of private data that is digitally sent, shared, received, and stored continues to burgeon.
This generates significant risk. Cybercriminals and rogue nation-states target private data at rest and in transit. Accordingly, proliferation of new technologies across the enterprise network, rapid adoption of cloud services, and multiplication of endpoints—including Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices—ratchets up risk and the complexity of protecting private data from malicious cyberattacks. A study by Ponemon Institute found that 82% of organizations believe they experienced at least one data breach due to digital transformation.
Annual industry studies such as the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report confirm that sensitive content remains in the crosshairs of bad actors. At the same time, according to the IBM and Ponemon Institute Cost of a Data Breach Report, the cost of a data breach—which includes damaged brand reputation, compliance fines and penalties, the loss of intellectual property (IP), and revelation of critical business information (e.g., legal cases, financial documents, manufacturing schedules, etc.)—continues to rise. The supply chain, which includes software, partners, and other third parties, is increasingly the root source of data breaches.
When it comes to sensitive content communications, the Kiteworks Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance Report found that 51% of organizations are inadequately protected against third-party security and compliance risks related to sensitive content communications.
The takeaway is that protecting your data and demonstrating compliance with relevant regulations has never been more difficult—and costly.
This blog post delves into some of the key cybersecurity and compliance insights for 2022 and the inferences we can make for the future.
Software Vulnerabilities
- According to the Check Point Cyber Security Report 2021, 75% of attacks in 2020 used vulnerabilities that were at least two years old. (Check Point)
- Q1 of 2022 witnessed more application-layer attacks than any other period in the preceding 12 months. (Cloudflare)
- DDoS vulnerabilities cost U.S. companies $218,000 on average before ransomware demands are made/paid. (Corero)
- One of the longest DDoS attacks early in 2022 lasted for an unbelievable 549 hours. (Kaspersky)
- The telecoms industry has been struck by the most network-layer assaults. (Cloudflare)
- Half of all vulnerabilities remain unresolved six months after discovery. (Veracode)
- 84% of companies have high-risk vulnerabilities on their network perimeter. (Positive Technologies)
- Three of the top 10 vulnerabilities most exploited in the U.S. by foreign actors are in Microsoft OLE. (CISA, FBI)
- One in five organizations do not test their software for vulnerabilities. (Ponemon Institute)
- 69% of malware today exploits zero-day vulnerabilities. (WatchGuard Technologies)
- Even a low-skilled attacker could exploit 10% of vulnerabilities by using a ready public exploit. (Positive Technologies)
- Half of the vulnerabilities can be eliminated by installing software updates. (Positive Technologies)
- Systems at 26% of companies are still vulnerable to WannaCry encryption malware. (Positive Technologies)
- 84% of companies are still vulnerable to the POODLE attack. (Positive Technologies)
- 20% of software vulnerabilities involved OpenSSH errors, which may allow attackers to obtain control over network perimeter resources or breach the company’s local network. (Positive Technologies)
Supply Chain
- 62% of attacks exploit the trust of customers in their suppliers. (European Union Agency for Cybersecurity)
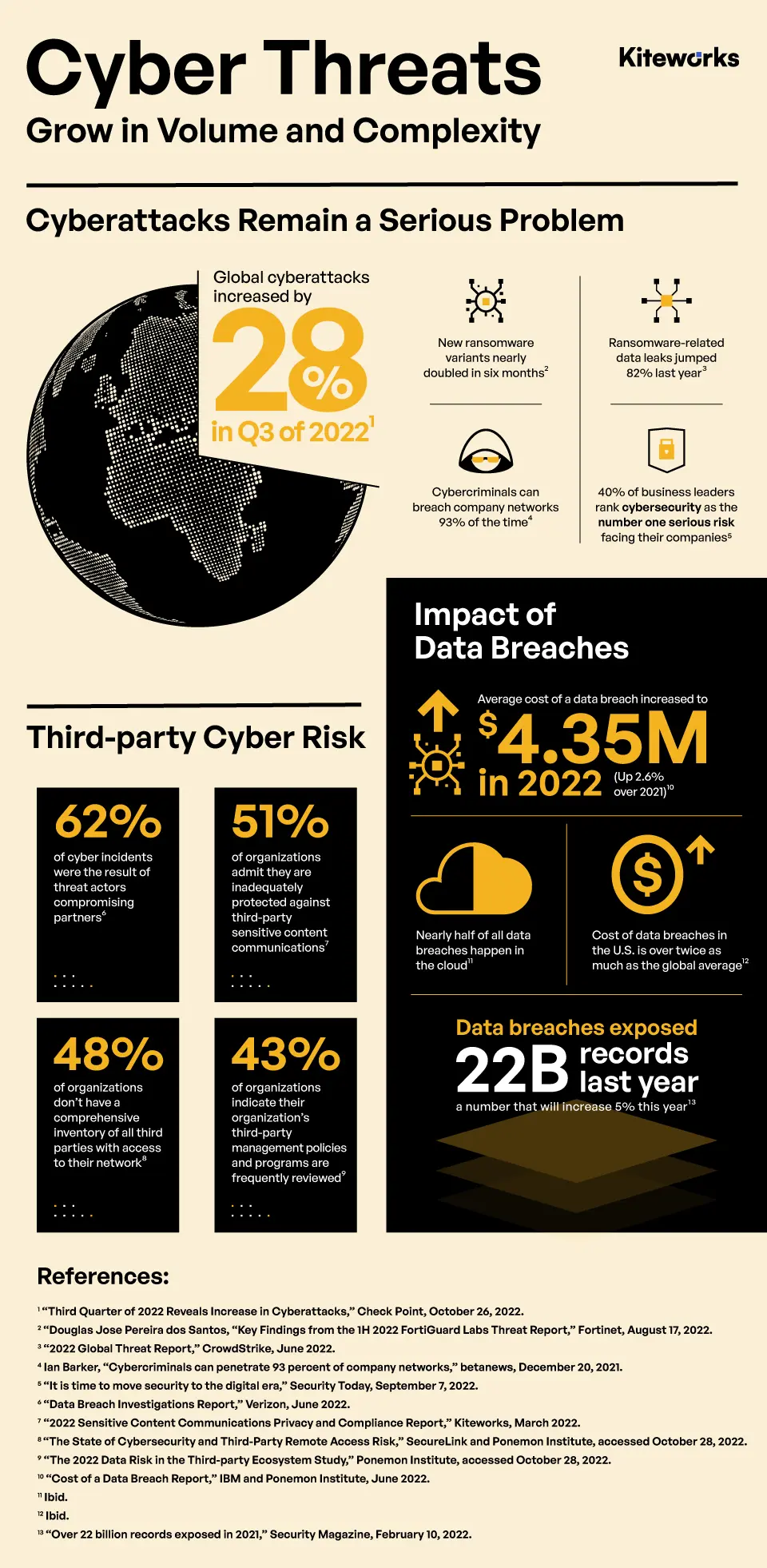
- 62% of cyber incidents involved threat actors compromising partners. (Verizon 2022 Data Breach Report)
- 48% of organization don’t have a comprehensive inventory of all third parties with access to their network. (SecureLink and Ponemon Institute)
- Only 36% of respondents in a CrowdStrike Global Attitude Survey had vetted new and existing suppliers for security purposes in the last 12 months. (CrowdStrike)
- 45% of organizations indicate they have been the victim of a supply chain attack in the past 12 months. (CrowdStrike)
- Supply chain attacks increased 100% year over year in 2021. (Symantec)
- More than half of all organizations will battle a software supply chain attack by 2025. (Gartner)
- $4.4 million—the cost of the Colonial Pipeline Co. hack, which exploited supply chain vulnerabilities. (Bloomberg)
- Global IoT connections expanded by 8% in 2022, totaling 12.2 billion active endpoints. (IoT Analytics)
Third-party Risks
- 51% of organizations are inadequately protected against third-party security and compliance risks. (Kiteworks)
- 67% of organizations use 4+ different systems to track, control, and secure content communications. (Kiteworks)
- 60% of organizations ask the sender to send an unencrypted file to a shared drive link if an email cannot be decrypted. (Kiteworks)
- 50%+ of organizations list HIPAA, PCI DSS, CCPA, GDPR, and DPA (France) as compliance regulations/standards with which they must comply. (Kiteworks)
- More than half of respondents indicate their organizations are inadequately prepared to address third-party risks related to confidential data sharing and storage. (Kiteworks)
- 88% of organizations do not encrypt all communications with third parties. (Kiteworks)
- 62% of cyber incidents involved threat actors compromising partners. (Verizon 2022 Data Breach Report)
- 48% of organizations don’t have a comprehensive inventory of all third parties with access to their network. (Ponemon Institute and SecureLink)
- 43% of organizations indicate their organization’s third-party management policies and programs are frequently reviewed. (Ponemon Institute and RiskRecon)
Ransomware
- CrowdStrike’s 2022 Global Threat Report reveals ransomware-related data leaks jumped 82% last year. (CrowdStrike)
- 495 million ransomware attacks occurred in the first nine months of 2021, representing a 148% increase from the previous year. (SonicWall)
- Over 37,700 ransomware attacks happen every hour globally. That is about 578 ransomware attacks each minute. (Matthew Woodward)
- 20% of Americans have dealt with a ransomware attack. (The Harris Poll)
- The average ransomware payment in 2021 was $570,000. (GRC World Forums)
- U.S. ransomware attacks cost an estimated $623.7 million in 2021. (Emsisoft)
- About 25% of all ransomware attacks target the manufacturing industry, with 17% targeting professional services and 13% government organizations. (Security Intelligence)
- In 2020, healthcare organizations paid $21 billion to ransomware attackers. (Comparitech)
- 3 out of 4 organizations have fallen prey to ransomware attacks, 64% paid ransom, while 40% were not able to recover their data. (Mimecast)
- 1,900—the number of distinct hacking groups active today. (FireEye Mandiant)
- A business falls victim to a ransomware attack every 14 seconds. (Cybersecurity Ventures)
- Many public services, including schools, healthcare services, and local U.S. municipal governments, were hit by ransomware attacks in early 2022. (TechTarget)
- The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency reported in February 2022 that ransomware incidents happened in 14 out of 16 critical U.S. infrastructure sectors. (CISA)
- According to a 2022 report, 88% of ransomware attacks attempted to infect backup repositories, and 75% of those attempts were successful. (Veeam)
- A ransomware attack in early 2020 on the New Orleans city government cost the city upwards of $7 million. (SC Magazine)
- In February 2020, a ransomware attack cost Denmark-based company ISS upwards of $50 million. (Asia Insurance Review)
- Ransomware attacks on U.S. healthcare organizations cost $7.8B in 2021. (Comparitech)
- Ransomware saw an almost 13% increase in 2022, a rise as big as the last five years combined. (Verizon 2022 Data Breach Report)
- Downtime and business interruption are the most dangerous aspects of a ransomware attack, more than the ransom itself. (Dark Reading)
- $5.2 billion worth of bitcoin transactions were estimated to be tied to ransomware payouts in 2021. (Financial Crimes Enforcement Network)
- Using a single password, hackers infiltrated the Colonial Pipeline Company in 2021 with a ransomware attack that caused fuel shortages across the U.S. (Bloomberg)
- Meat processing company JBS was the victim of a ransomware attack that shut down beef and poultry processing plants on four different continents. (Wall Street Journal)
Cyberattacks
- At least 50% of consumers have experienced cybercrime, with about 33% falling victim in 2021. (Norton)
- 68% of business executives feel their cybersecurity risks are increasing. (Accenture)
- 212 days was the average time to detect a cyberattack in 2021. (IBM)
- $6.1 trillion—estimated global cost of cybercrime in 2021 expected to grow 15% year-over-year, reaching $10.5 trillion by 2025. (Cybersecurity Ventures)
- Around 20% of phishing email reaches worker inboxes, demonstrating that attackers continue to get better and more sophisticated dodging security training and processes. (Dark Reading)
- Security services accounted for an estimated 50% of cybersecurity budgets in 2020. (Gartner)
- Less than 50% of organizations apply zero-trust security principles to file transfer and automation, web forms, and APIs. (Kiteworks)
- 50% of large enterprises (with over 10,000 employees) are spending $1 million or more annually on security, with 43% spending $250,000 to $999,999, and just 7% spending under $250,000. (OEM Magazine)
- 18% of CEOs said that cybersecurity risk would be the biggest threat to their organization’s growth through 2024. (KPMG)
- Google announced it will invest $10 billion over the next five years to expand zero-trust programs and help 100,000 Americans acquire industry-recognized digital skills. (White House)
- IBM announced it will train 150,000 people in cybersecurity skills over the next three years. (White House)
- By 2023, there will be 3x more networked devices on Earth than humans. (Cisco)
- By the end of 2022, 1 trillion networked sensors will be embedded in the world around us, with up to 45 trillion in 15 years. (Cisco)
- 100 million lines of code and 100 electronic control units are the numbers in a modern autonomous vehicle. These figures are expected to triple by 2030. For context, a modern passenger jet has 15 million lines of code. (McKinsey & Company)
- 66% of small and medium-sized businesses had at least one cyber incident in the past two years. (Forbes)
- 39% of security technologies used by organizations are outdated. (Cisco)
- Crypto mining, phishing, ransomware, and trojans averaged 10x the internet activity of all other threat types. (Cisco)
- Network perimeters are at risk 93% of the time. (Positive Technologies)
- More than a third of organizations saw an uptick in cyberattacks over 2021. (ISACA)
- The retail sector loses $38,052 every minute from cybercrime, while healthcare organizations spend $13 a minute on data breaches. (Cloud Security Alliance)
- 9% of employees take more than one hour to flag a phishing email. (Cofense)
- 26% of security professionals don’t have an automated tool to spot and stop endpoint attacks. (Check Point)
- Global attacks increased by 28% in the third quarter of 2022 compared to same period in 2021. (Check Point)
- The most common attack vector is credential theft (19%) then phishing (16%), followed by misconfigured cloud (15%) and vulnerabilities in third-party software (13%). (IBM and Ponemon Institute)
- The average weekly attacks per organization worldwide reached over 1,130. (Check Point)
- 31% increase in the average number of attacks per company since 2020. (Accenture)
- 32% of organizations admit security is not part of the cloud discussion and that they are playing catch-up. (Accenture)
- The global cost of online crime will reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. (Cybersecurity Ventures)
- Businesses suffered 50% more cyberattack attempts per week in 2021. (Dark Reading)
- Cybercriminals can penetrate 93% of company networks. (Positive Technologies)
- 40% of small businesses that have faced a severe cyberattack experienced at least 8 hours of downtime. (Cisco)
- 83% of small and medium-sized businesses are not financially prepared to recover from a cyberattack. (Insurance Bee)
Data Breaches
- 95% of cybersecurity breaches can be attributed to human error. (World Economic Forum)
- Around 90% of data breaches are financially motivated. Espionage, which is in second place, is dramatically lower. (Verizon 2022 Data Breach Report)
- $4.35 million per attack—the average cost of a data breach in the United States in 2022. (IBM and Ponemon Institute)
- 20% of all data breaches involve an internal actor. (Verizon 2022 Data Breach Report)
- 700,000—the number of cybersecurity job openings in the United States in April 2022, with the unfilled positions rising globally to 3.5 million by 2025. (CyberSeek)
- About 40% of the world’s population is offline at any given moment, exposing them to cyberattacks when they try to connect again. (DataReportal)
- 42% of companies suffer from cyber fatigue/apathy, affecting their ability to defend against cyberattacks. (Cisco)
- 40% of ransomware incidents involve the use of desktop sharing software and 35% involve the use of email. (Verizon 2022 Data Breach Report)
- In 2021, nearly 40% of breaches featured phishing, around 11% involved malware, and about 22% involved hacking. (Verizon 2021 Data Breach Report)
- 82% of data breaches involve the human element and consisted of stolen credentials, phishing, misuse, or simply error. (Verizon 2022 Data Breach Report)
- 300 billion—the estimated number of passwords used by humans and machines worldwide. (Cybersecurity Ventures)
- 50% of breaches are accredited to insecure remote access and web applications. (Verizon 2022 Data Breach Report)
- Since the pandemic began, 20% of business leaders have borne the effects of a data breach caused by a remote worker. (Malwarebytes Labs)
- $120,000—the average cost of a cyber incident to a small business. (Insurance Bee)
- 44% of respondents believe that cyber incidents and data breaches are the top concerns for business in 2022, ahead of business interruption and natural catastrophes. (Allianz Risk Barometer)
- 25% of Ultra High Net Worth Individuals with an average wealth of $1 billion have been targeted by cybercriminals for their data. (Barclays Private Bank)
- There were 153 million new malware samples from March 2021 to February 2022. (AV-TEST Institute)
- Phishing attacks were connected to 36% of breaches. (Verizon 2022 Data Breach Report)
- The number of healthcare breaches in the first five months of 2022 almost doubled when compared to the same period in 2021, according to the U.S. government. (TechTarget)
- Data breaches exposed 22 billion records in 2021—a number that will increase 5% this year. (Risk Based Security)
- Nearly 48 million people had their personal information stolen in a 2021 T-Mobile data breach. (T-Mobile)
- Personal data belonging to more than 100 million Android users was exposed in a 2021 data leak due to misconfigured cloud services. (Check Point)
- GDPR fines totaled $1.2 billion in 2021. (CNBC)
- Organizations with a zero-trust approach saw average breach costs of $1.76 million less than organizations without. (IBM and Ponemon Institute)
- The average cost per breach is $1.07 million higher when remote work is a factor. (IBM and Ponemon Institute)
- Nearly half of all data breaches happen in the cloud. (IBM and Ponemon Institute)
- Cost of data breaches in the U.S. is over twice as much as the global average. (IBM and Ponemon Institute)
- Education was the most targeted industry sector with the most cyberattacks in the third quarter of 2022 (18%). (Check Point)
Managing Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance Risk
These top cybersecurity stats for 2022 demonstrate that cybersecurity remains a critical focus for the private and public sectors. When private data is breached, stolen, or held for ransom, the detrimental implications to organizations and personal repercussions are significant. Organizations experience operational, reputational, and financial impact that easily spiral into the millions of dollars. Some small and medium-sized businesses are unable to recover and go out of business.
Sensitive content communications present bad actors with a lucrative cyber target. Personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), financial documents, merger and acquisition (M&A) communications, IP, and other forms of private data are some of the primary types of sensitive content in purview. In response, government entities and industry groups have issued a series of regulations and standards, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which require organizations to comply with governance tracking and control.
Thousands of global organizations rely on the Kiteworks Private Content Network to address these privacy and compliance challenges—unifying, tracking, controlling, and securing sensitive content communications. Schedule a custom demo to see how the Kiteworks Private Content Network can enable you to manage governance and security risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
Cybersecurity Risk Management is a strategic approach used by organizations to identify, assess, and prioritize potential threats to their digital assets, such as hardware, systems, customer data, and intellectual property. It involves conducting a risk assessment to identify the most significant threats and creating a plan to address them, which may include preventive measures like firewalls and antivirus software. This process also requires regular monitoring and updating to account for new threats and organizational changes. The ultimate goal of Cybersecurity Risk Management is to safeguard the organization’s information assets, reputation, and legal standing, making it a crucial component of any organization’s overall risk management strategy.
The key components of a Cybersecurity Risk Management program include risk identification, risk assessment, risk mitigation, and continuous monitoring. It also involves developing a cybersecurity policy, implementing security controls, and conducting regular audits and reviews.
Organizations can mitigate cybersecurity risks through several strategies. These include implementing strong access control measures like robust passwords and multi-factor authentication, regularly updating and patching systems to fix known vulnerabilities, and conducting employee training to recognize potential threats. The use of security software, such as antivirus and anti-malware programs, can help detect and eliminate threats, while regular data backups can mitigate damage from data breaches or ransomware attacks. Having an incident response plan can minimize damage during a cybersecurity incident, and regular risk assessments can identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Lastly, compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standards, can further help organizations mitigate cybersecurity risks.
A risk assessment is a crucial part of Cybersecurity Risk Management. It involves identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities, assessing the potential impact and likelihood of these risks, and prioritizing them based on their severity. This helps in developing effective strategies to mitigate these risks.
Continuous monitoring is a vital component of Cybersecurity Risk Management, providing real-time observation and analysis of system components to detect security anomalies. This enables immediate threat detection and response, helping to prevent or minimize damage. It also ensures compliance with cybersecurity standards and regulations, allowing organizations to quickly address any areas of non-compliance. By tracking system performance, continuous monitoring aids in identifying potential vulnerabilities, while the data gathered informs decision-making processes about resource allocation, risk management strategies, and security controls.
Additional Resources
- Report Benchmark Your Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance
- Blog Post Key Takeaways from the IBM and Ponemon Institute Cost of a Data Breach Report
- Blog Post Key Findings from the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report
- Blog Post What is a SOC2 Report?
- Glossary Risk And Security Management
- Blog Post What is Governance in Security
- Glossary Cybersecurity Maturity Level
- Glossary Managing Cybersecurity Risk