Comprehensive Guide to the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act
The Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act (referred to as “Indiana CDPA” or “the Act”) is a comprehensive state-level data privacy law that aims to provide consumers residing in the state of Indiana with more control over their personal information. The Act is set to become the seventh state to pass a comprehensive privacy law in the United States. The Indiana CDPA is inspired and influenced by several other privacy laws, including California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA), and Colorado Privacy Act (CPA). The Act takes effect on January 1, 2026.

The Act establishes new rights for consumers to access, delete, or opt out of the sale or sharing of their personal information. It also imposes new obligations on businesses to protect consumer data, provide transparency about data collection and usage practices, and maintain data security. This article delves into the details of the Indiana CDPA, providing a comprehensive guide on what businesses need to know to comply with the new law.
Who Is Covered by the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act?
The Indiana CDPA applies to businesses that meet certain thresholds, namely those that:
- Control or process the personal data of at least 25,000 Indiana residents; or
- Derive over 50% of their gross revenue from the sale of Indiana residents’ personal data and control or process the personal data of at least 5,000 Indiana residents.
The Indiana CDPA does not apply to certain organizations, including state or local government entities, certain financial institutions subject to the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), or covered entities under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Additionally, employee data and business-to-business data are generally exempt from the Act’s requirements.
What Is Personal Data Under the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act?
Under the Indiana CDPA, personal data is defined as any information that can be associated with, linked to, or capable of being linked to an individual. This may include information such as names, addresses, email addresses, Social Security numbers, and more. The Act also includes special provisions for sensitive data, which includes data related to race, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, biometric or genetic data, and geolocation data.
Consumer Rights Under the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act
With the Indiana CDPA signed into law, Indianans now enjoy several unalienable rights designed to protect their data privacy. The consumer rights under the Indiana CDPA include:
Right to Know and Access
Indiana consumers have the right to request and obtain information about the personal data that businesses collect, use, share, or sell. Businesses must respond to such requests within 45 days, providing consumers with a report that includes details on the categories of personal data collected, the purposes of collection, and with whom the data is shared or sold.
Right to Delete
Consumers have the right to request the deletion of their personal data, subject to certain exceptions. Businesses must promptly delete the data upon receiving a valid request and notify third parties to whom the data was disclosed, if applicable.
Right to Opt Out
Consumers have the right to opt out of the sale or sharing of their personal data for targeted advertising. Businesses must provide a clear and conspicuous method for consumers to opt out and must respect the consumer’s choice.
Right to Nondiscrimination
Businesses are prohibited from discriminating against consumers who exercise their rights under the Indiana CDPA. Discrimination may include denying goods or services, charging different prices or rates, providing a different level of quality, or suggesting any of the above actions will occur.
Business Obligations Under the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act
The Indiana CDPA imposes several legally binding obligations on businesses that collect, process, or share personal information of Indiana residents, including:
Transparency and Notice Requirements
Businesses must provide clear and conspicuous notices to consumers about their data collection and usage practices. These notices should include a description of the consumer’s rights, the categories of personal data collected, the purposes of collection, any third parties with whom the data is shared or sold, and instructions for submitting requests related to personal data.
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
The Indiana CDPA requires businesses to collect only the minimum amount of personal data necessary to fulfill the purposes for which the data was collected. Businesses must also ensure that the use of personal data is limited to the specific purposes disclosed to the consumer.
Data Security
Businesses are required to implement reasonable security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, disclosure, or destruction. The Act does not provide specific guidance on what constitutes reasonable security measures, but businesses should consider industry best practices and their specific risk factors when developing and maintaining data security programs.
Data Protection Assessments
Businesses must conduct data protection assessments for certain high-risk data processing activities, such as the sale of personal data, targeted advertising, or the processing of sensitive data. These assessments should evaluate the risks and benefits of the data processing activities and consider the potential impact on consumer privacy.
Contractual Requirements With Service Providers
Businesses that share personal data with service providers must enter into contracts that include certain provisions, such as the service provider’s agreement to comply with the Indiana CDPA, restrictions on the use of personal data for purposes other than those specified in the contract, and requirements for the service provider to implement and maintain appropriate data security measures.
Similarities and Differences Between the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act and Other State and Federal Laws
Indiana is one of several states that have data privacy laws protecting their residents. Not surprisingly, several other state and federal privacy laws share similarities with the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act, including:
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a comprehensive privacy law that provides California residents with rights similar to those under the Indiana CDPA, such as the right to access, delete, and opt out of the sale of their personal information. However, there are key differences, such as the CCPA’s broader definition of “sale” and its higher thresholds for applicability to businesses.
Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act
The Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) also offers similar consumer rights and protections, but it does not include a private right of action, relying solely on the enforcement authority of the Virginia Attorney General.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is more extensive and stringent than the Indiana CDPA, with more robust consumer rights, obligations for businesses handling personal information, and stricter penalties for noncompliance.
Other State Privacy Laws
Several other states, such as Colorado, Connecticut, and Nevada, have enacted privacy laws that share similarities with the Indiana CDPA but may differ in scope, definitions, and requirements. For a map and full list of states who have proposed, passed, or signed a data privacy law, and more information on each, click here.
Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act Compliance Strategies for Businesses
To comply with the Indiana CDPA, businesses must take several steps, including:
| Step 1 | Review and update privacy policies and notices to ensure they clearly and accurately describe data processing activities and comply with the Act’s requirements. |
| Step 2 | Implement processes to respond to consumer requests to access, delete, or opt out of the sale or sharing of consumers’ personal information. |
| Step 3 | Ensure the appropriate data security measures are in place to protect personal information from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. |
| Step 4 | Conduct regular risk assessments and update all data processing activities as necessary to mitigate identified risks. |
| Step 5 | Appoint a data protection officer, if required, to oversee compliance with the Act and establish a comprehensive privacy program that includes training for employees and regular audits and assessments of data processing activities. |
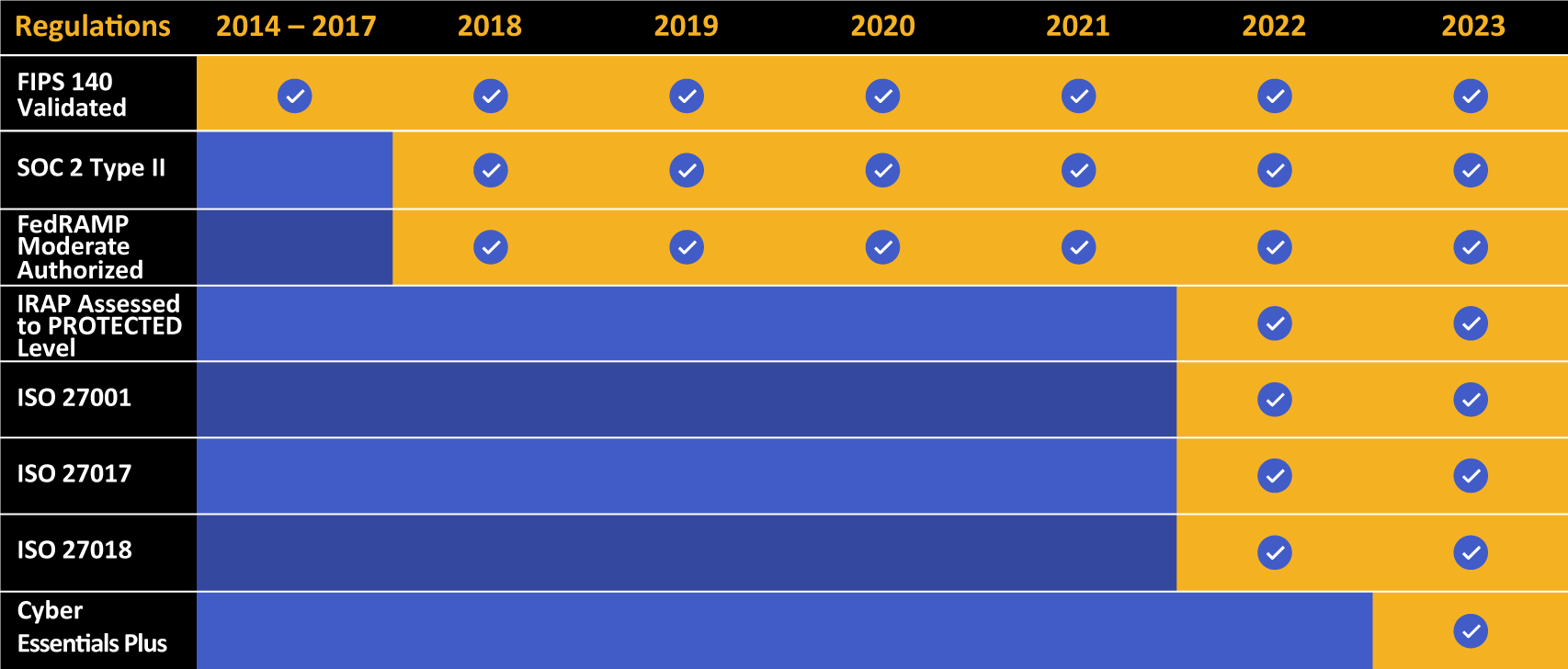
Kiteworks touts a long list of compliance and certification achievements.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Indiana CDPA
1. What is the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act, and what does it aim to accomplish?
The Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act is a comprehensive privacy law that seeks to protect the personal information of Indiana residents. The Act applies to any company that collects, processes, or retains personal information about Indiana residents, regardless of where the company is located. The Indiana CDPA aims to give Indiana residents greater control over their personal information and requires companies to implement measures to protect against data breaches and maintain the security and confidentiality of personal information.
2. What types of personal information are covered by the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act?
The Indiana CDPA covers a broad range of personal information, including but not limited to names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, Social Security numbers, driver’s license numbers, passport numbers, biometric data, health information, financial information, and online browsing and search history. The Act also covers information regarding a consumer’s interactions with a business, such as purchase history, customer service inquiries, and marketing preferences.
3. What are the key requirements for companies under the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act?
Under the Indiana CDPA, companies are required to obtain affirmative consent from consumers before collecting, processing, or disclosing their personal information. Companies must also provide consumers with certain rights related to their personal information, such as the right to access, delete, and correct their personal information. Companies must implement reasonable security measures to protect against data breaches and must notify consumers and the Indiana Attorney General’s Office in the event of a data breach that affects more than 500 Indiana residents. Companies are also required to conduct data protection assessments and implement data retention and data minimization policies.
4. What are the penalties for noncompliance with the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act?
The Indiana CDPA provides for civil penalties of up to $5,000 per violation, with a maximum penalty of $500,000 per incident. In addition, the Indiana Attorney General’s Office may bring an action to enjoin a violation of the Act or to obtain damages on behalf of affected consumers. Companies may also face reputational harm and loss of consumer trust in the event of a data breach or violation of the Indiana CDPA.
5. How does the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act compare to other state privacy laws?
The Indiana CDPA is one of several state privacy laws that have been enacted in recent years, including the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA), and the Colorado Privacy Act (CPA). While there are similarities among these laws, the Indiana CDPA has some distinct provisions that set it apart. For example, the Indiana CDPA requires companies to conduct data protection assessments, which are not required under the CCPA or VCDPA. The Indiana CDPA also requires companies to implement data retention and data minimization policies, which are not explicitly required under the other state laws. Additionally, the penalties for noncompliance with the Indiana CDPA are lower than those under the CCPA or VCDPA, but higher than those under the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA). Overall, the Indiana CDPA reflects a growing trend toward comprehensive state privacy laws, and companies will need to carefully consider their obligations under each applicable law.
Kiteworks Helps Businesses Comply With the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act
Sensitive content communications are a vital part of ensuring compliance to regulations such as the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act. To effectively protect personally identifiable information (PII) of Indiana residents, private sector businesses must have a system in place to track, control, and secure digital communications of PII. In the past, companies have relied on multiple tools and approaches to manage the different communications channels, such as email, file sharing, and application programming interfaces (APIs), leading to a fragmentation of metadata that makes it hard to maintain, protect, and control a centralized and automated system.
The Kiteworks Private Content Network allows organizations to consolidate their sensitive communications involving PII, including email, managed file transfer, file sharing, web forms, and more. With Kiteworks, organizations track, control, and secure sensitive data shared and sent in and out of their organizations—all helping to ensure Indiana CDPA compliance.
Kiteworks provides businesses several features to protect customers’ PII. For example, all data in transit and at rest is encrypted to ensure maximum security. Robust access controls limit who can access sensitive PII and role-based permissions control who can download, edit, or just view this and other content. In accordance with “right to be forgotten” principles, Kiteworks allows for the erasure of PII when necessary. With the remote wipe feature, organizations can erase data from lost or stolen devices, further safeguarding PII. Lastly, Kiteworks employs digital rights management (DRM) capabilities to prevent unauthorized data dissemination, enhancing Indiana CDPA compliance.
Schedule a custom demo today to learn about the Kiteworks Private Content Network and how it can help your organization comply with the Indiana CDPA and other state privacy laws.

