The Benefits of Obtaining Cyber Essentials Certification
Cyber Essentials is a security certification designed to help organization rotect their systems, networks, and data from cyberattacks. It is based on five fundamental security principles and provides organizations with increased system and data security, improved regulatory compliance, and reduced cost of implementing cybersecurity measures.

Overview of the Importance of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a critical component of modern information systems and networks. With the increasing number of cyberattacks, organizations need to implement measures that protect their data and systems from these attacks. Cyber Essentials is one such measure that organizations can use to ensure they are protected from cyberattacks and adhere to data protection and compliance standards.
What Is Cyber Essentials Certification?
Launched by the United Kingdom Government’s National cybersecurity Centre in 2014, Cyber Essentials is a security certification designed to help organizations protect their systems, networks, and data from cyberattacks. It is based on five fundamental security principles that include understanding the threats and risks associated with cybersecurity, protecting computers and networks against malicious software and other online threats, checking the strength of passwords and other authentication measures, setting up firewalls, and training staff on cybersecurity best practices. There are two levels of certification: Cyber Essentials Basic and Cyber Essentials Plus.
Who Does Cyber Essentials Apply To?
Cyber Essentials certification applies to all organizations regardless of size, sector, or geographic location. This certification is designed to help organizations protect themselves against the most common cyber threats by implementing basic security controls. It is a government-backed scheme that provides a clear statement of the basic controls organizations should have in place to protect themselves from the most common cyber threats.
Is it a requirement to have Cyber Essentials for the General Data Protection Regulation?
No, Cyber Essentials is not a requirement for the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), though it may help businesses meet certain GDPR requirements. The GDPR, for example, outlines a number of requirements related to data security, privacy, and data protection that must be met. Cyber Essentials, by contrast, is an industry-recognized certification scheme that provides guidance and tools to help organizations achieve basic levels of cybersecurity.
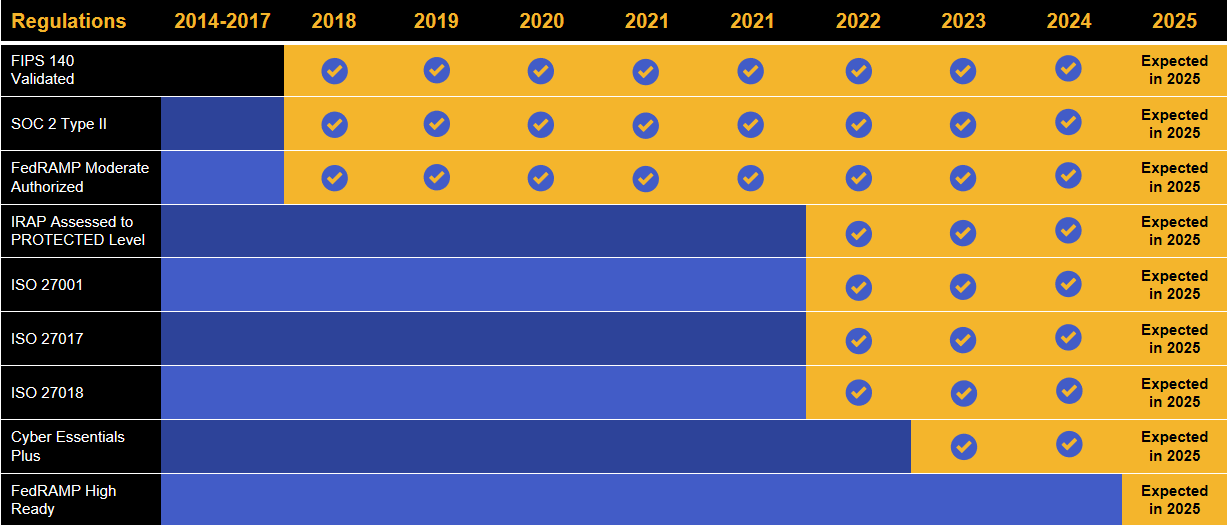
Kiteworks touts a long list of compliance and certification achievements.
Benefits of Implementing Cyber Essentials
Cyber Essentials is a proven cybersecurity framework that provides organizations of all sizes with essential security controls and business benefits including:
Increased system and data security
One of the primary benefits of obtaining Cyber Essentials certification is the increase in system and data security. By implementing the necessary measures recommended in the framework, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to cyberattacks and protect their systems and data from being compromised.
Improved compliance with GDPR and other existing regulations
Cyber Essentials certification helps organizations meet the requirements of the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other existing regulations regarding data protection. This form of certification ensures that organizations have implemented the necessary technical and organizational measures to protect their data from unauthorized access or malicious activities.
Reduced cost of implementing cybersecurity measures
Implementing cybersecurity measures can be an expensive process for organizations. However, with Cyber Essentials certification, organizations can reduce the cost of implementing such measures as the scope of the certification is limited to the five primary security principles.
What Does Cyber Essentials Entail?
Cyber Essentials certification comprises five essential security controls. Organizations that have achieved Cyber Essentials certification have been assessed by an external party against these five essential security controls. The controls include:
Understanding cybersecurity threats and risks
The first step to implementing Cyber Essentials is to understand the various cyber threats and risks. This includes understanding how cyberattacks are launched, what type of malicious software is used, and how organizations can best protect their data and systems from such attacks.
Protecting computers and networks against malicious software and other online threats
Once organizations have identified the cybersecurity threats and risks in their business, they can begin to implement measures to protect their systems and data, as well as sensitive content communications. This includes using strong passwords, setting up firewalls, and implementing antivirus software.
Improving password strength and other authentication measures
To ensure that passwords are secure, organizations should use a password manager that checks password strength and other authentication measures like multi-factor authentication. This is important to prevent the unauthorized access of confidential information.
Setting up firewalls
Firewalls are critical for protecting networks from cyberattacks and malicious activities. Organizations should ensure that their networks are secured with the latest firewalls and are regularly monitored for any suspicious activity.
Training staff on cybersecurity best practices
Organizations should also ensure that their staff are regularly trained on the best and most current cybersecurity practices. This includes educating them on how to identify potential threats and how to protect their systems and data from being compromised.
What’s the Difference Between Cyber Essentials and Cyber Essentials Plus?
Cyber Essentials and Cyber Essentials Plus are two certifications and businesses can choose which one to pursue based on their individual needs. The Cyber Essentials scheme is a basic level framework of security controls that are laid out as five key controls. Cyber Essentials Plus is an extension of the scheme and was developed in 2014 as a more advanced certification. Both demonstrate a commitment to cybersecurity; however, Cyber Essentials Plus requires more work and therefore demonstrates a greater commitment to cybersecurity.
The main difference between Cyber Essentials and Cyber Essentials Plus is that Cyber Essentials is self-assessed, while Cyber Essentials Plus is externally verified by an external assessor. Cyber Essentials, for example, requires an organization to answer a few questions and complete an online self-assessment questionnaire. Cyber Essentials Plus, by contrast, involves an external certification body conducting an on-site assessment of the organization’s security systems and procedures.
In terms of criteria , Cyber Essentials requires organizations to have adequate defenses against the most common cyber threats. This includes strong user access and device security controls, firewalls and internet gateways, malware protection, and secure configuration. Cyber Essentials Plus goes further and requires organizations to provide evidence that these controls are operating effectively, and additional controls are in place, such as patch management and secure configuration for mobile devices.
Cyber Essentials Plus also requires organizations to have in place a comprehensive set of cybersecurity policies and procedures. These include risk assessment processes, incident response plans, and employee awareness training policies. This additional layer of security is important for organizations looking to demonstrate a higher commitment to cybersecurity and helps protect themselves against more sophisticated attacks.
Overall, Cyber Essentials and Cyber Essentials Plus offer organizations of any size, industry, or location the ability to show their commitment to cybersecurity and ensure that their data and networks are adequately protected.
Estimating the Cost of Cyber Essentials Certification
Understanding the cyber essentials certification cost is crucial for organizations planning their cybersecurity investment. For Cyber Essentials basic certification, the cost typically ranges from £300 to £500 annually, depending on the certification body and organization size. This includes the self-assessment questionnaire and validation by an IASME Certification Body approved assessor. The cyber essentials certification cost for the Plus variant is significantly higher, ranging from £1,500 to £4,000, due to the additional technical verification and hands-on testing required.
Several factors influence the overall costs beyond the basic certification fees. Internal preparation expenses include staff time for completing documentation, implementing required security controls, and addressing any gaps identified during pre-assessment. Organizations should budget 20-40 hours of internal effort for basic certification and 60-120 hours for Plus certification. Additional costs may arise from necessary infrastructure upgrades, software licensing for security tools, and potential consultant fees for complex environments.
To optimize costs while maintaining certification integrity, organizations should conduct thorough internal readiness assessments before formal submission. This helps identify and resolve issues early, reducing the likelihood of costly re-assessments. Choosing the appropriate certification level based on genuine business requirements rather than perceived prestige also ensures cost-effectiveness. Regular maintenance of security controls throughout the year prevents expensive last-minute remediation work during renewal periods.
How to Get Certified With Cyber Essentials
Cyber Essentials certification mandates that organizations must take a number of steps to protect their data and systems from cyber threats. This includes securing their network perimeter, implementing security policies, using antivirus software, patching systems and networks, and using encryption to protect information. Once organizations have a clear understanding of the objectives of the certification, they can then begin the process of getting certified. These steps include:
Register your organization with the IASME Certification Body
To become certified with Cyber Essentials, organizations must first register with the IASME Certification Body. This independent organization is responsible for verifying that organizations that wish to gain Cyber Essentials certification are compliant with the Cyber Essentials standard. This process includes checking that the company has implemented the technical controls and policies that are required as part of the certification. IASME reviews the technical information and evidence submitted by the organization, including the completed self-assessment questionnaire. IASME also provides feedback and guidance on areas where the organization may need to make changes to meet the requirements of the standard. IASME is also responsible for ensuring that the certification is reliable and consistent across different organizations.
Complete an online questionnaire detailing the implementation of cybersecurity measures
Organizations must complete an online questionnaire detailing the measures that have been implemented to protect their systems and data from cyberattacks. This questionnaire will probe organizations on their use of firewalls, antivirus software, and other security measures.
Have your IT systems reviewed and assessed by a third-party organization
After completing the questionnaire, organizations seeking Cyber Essentials Plus must have their IT systems reviewed and assessed by an independent third-party organization. This is to ensure that their systems meet the necessary security requirements as outlined by Cyber Essentials.
Certification Validity and Renewal Timeline
Cyber essentials certification has a validity period of exactly one year from the date of issue, after which organizations must undergo the full certification process again to maintain their cyber essentials accreditation. This annual renewal requirement ensures that security controls remain current and effective against evolving cyber threats. Organizations should begin planning for renewal at least three months before expiration to avoid any gaps in certification status, particularly important for those requiring continuous cyber essentials compliance for government contracts or business partnerships.
Certain circumstances may trigger the need for earlier reassessment before the standard annual renewal. Significant infrastructure changes, such as major system upgrades, network redesigns, or substantial increases in scope, require immediate re-certification to ensure the cyber essentials certificate remains valid. Organizations moving premises, implementing new cloud services, or undergoing mergers and acquisitions should consult with their certification body to determine if early reassessment is necessary.
To maintain compliance between renewal cycles, organizations should implement continuous monitoring of their security posture, conduct quarterly policy reviews, and maintain detailed records of any changes to their IT environment. Regular vulnerability assessments, prompt patch management, and ongoing staff training help ensure that cyber essentials requirements are consistently met. This proactive approach not only supports smooth renewals but also maximizes the benefits of cyber essentials by maintaining robust security throughout the certification period.
Preparing for a Cyber Essentials Plus Audit
Successful preparation for a Cyber Essentials Plus audit requires systematic evidence collection and technical verification readiness. Begin by gathering comprehensive documentation including network diagrams, asset inventories, patch management records, and security policy documents. Ensure all systems are running current vulnerability scans and address any critical or high-risk findings before the audit date. The external assessor will require remote access to sample devices, so prepare a representative selection of workstations, servers, and mobile devices that accurately reflect your organization’s IT environment.
Timeline planning is crucial for audit success. Allow 6-8 weeks for comprehensive preparation, including 2-3 weeks for initial gap analysis, 3-4 weeks for remediation activities, and 1 week for final verification testing. Common pitfalls include inadequate patch management documentation, misconfigured firewall rules, and insufficient malware protection coverage. Verify that all user accounts have appropriate access controls, remove any unnecessary administrative privileges, and ensure mobile device management policies are properly enforced across all relevant devices.
On audit day, ensure key technical staff are available to assist the assessor and answer questions about system configurations. Prepare a quiet workspace with reliable internet connectivity for the remote assessment activities. Have contact details for system administrators readily available and ensure all sample devices are powered on and accessible. Remember that the assessor may spend 4-8 hours conducting technical testing, so plan accordingly to minimize business disruption while ensuring full cooperation with the certification process.
Define Your Certification Scope
- Identify all network boundaries and internet-facing systems that require protection under the certification, including main office networks, remote worker connections, and any cloud services that store or process business data
- Map all user devices within scope, including desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and smartphones used for business purposes, while clearly documenting any excluded systems such as isolated networks or legacy equipment
- Document third-party connections and shared services, determining whether managed service providers, partner networks, or supplier systems fall within your certification boundary or are appropriately excluded with justification
- Review IASME and NCSC guidance documents to ensure your scope definition aligns with certification requirements and includes all systems that could provide an attacker pathway into your core business environment
- Create a comprehensive scope statement documenting included and excluded systems, with clear rationale for exclusions, to provide cyber essentials scope statement examples for future reference and auditor review
- Validate scope decisions with technical teams and business stakeholders to ensure nothing critical is overlooked while avoiding unnecessary complexity that could increase costs or certification timelines


