Guide
Kiteworks’ Guide to the Saudi Data and Artificial Intelligence Authority (SDAIA) National Data Governance Interim Regulations
Interim Regulations on Data Classification, Protection, Sharing, and Open Data
Introduction
The Saudi Data and Artificial Intelligence Authority (SDAIA) is the authority in Saudi Arabia concerned with data and AI, including big data. The SDAIA has created a data governance framework at the national level that outlines the laws and regulations for national data management and governance as well as the protection of personal data. The National Data Governance Interim Regulations were published in 2020 to govern the collection, use, processing, and management of data in the region. The regulations are considered interim, indicating that the regulation of data will continue to evolve as the SDAIA and National Data Management Office (NDMO) grow more established. The National Data Governance Interim Regulations document covers rules and obligations related to data classification, data sharing, data privacy, freedom of information, and open data. The regulations set the framework for classifying the data received, produced, or dealt with by public entities, regardless of their source, form, or nature. The implementing regulation sets out the bases for the protection of personal data, the rights of data subjects, and the obligations of controllers. The regulations regulate the sharing of data produced by government entities with other government entities, private entities, and individuals.
SDAIA Interim Regulations
- Data Classification
- Personal Data Protection
- Data Sharing
- Freedom of Information
- Open Data
The National Data Governance Interim Regulations provide a framework for national data management and governance policies and controls, protect personal data, and increase the value learned from it in order to make strategic decisions, anticipate the future, and uphold the highest standards of accountability and transparency. The regulations cover five topics: data classification by public entities, protection of personal data, data sharing between public entities, freedom of information requests, and open data. The SDAIA enforces the law through binding and non-binding measures, including compliance certification, and has launched the Data and AI Ethics and Policy Observatory to ensure that the development and use of data and AI technologies in the Kingdom are ethical, transparent, and aligned with the Kingdom’s values and principles.
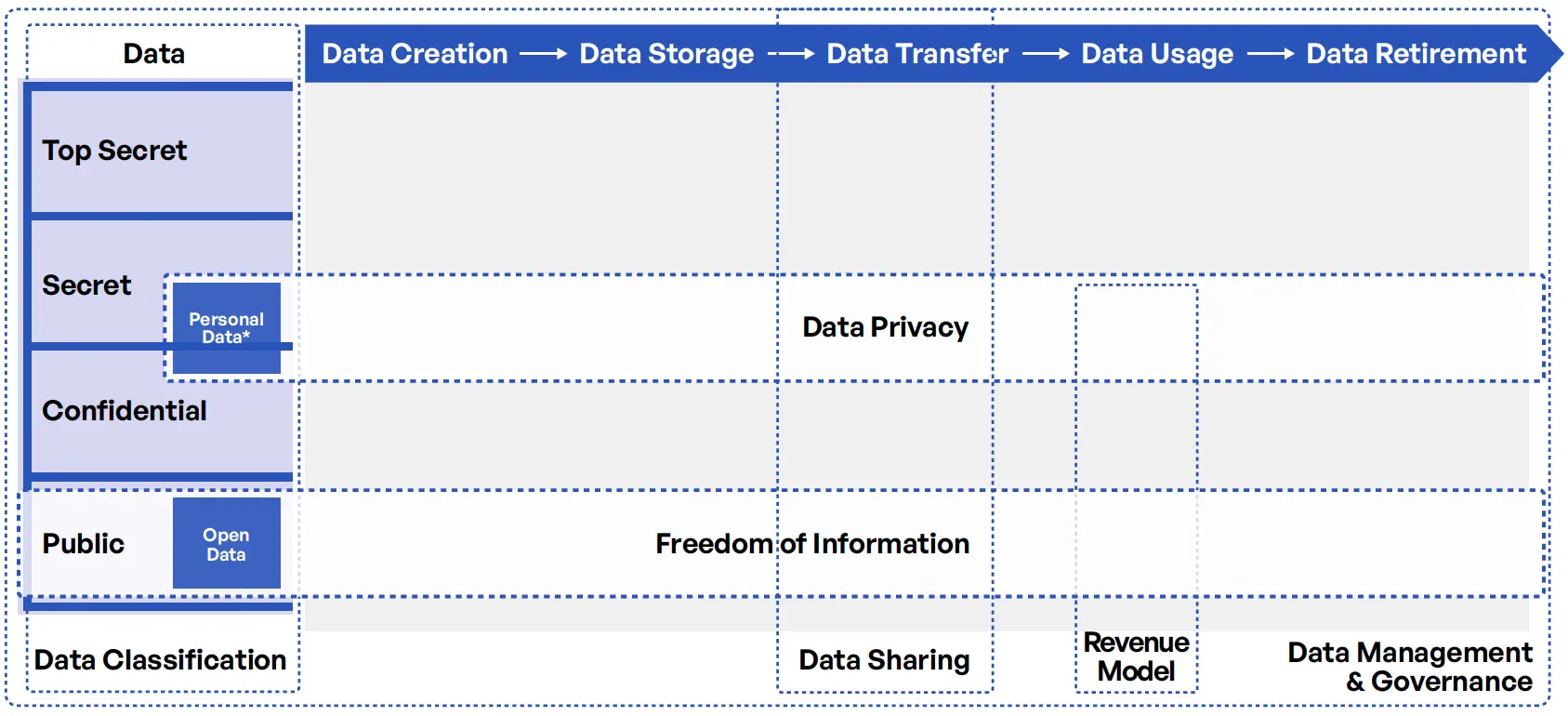
(*) May be classified as Top Secret
This guide showcases how Kiteworks can support public entities handling personal data comply with specific sections of the Interim guidelines to achieve comprehensive data governance of their critical unstructured data.
The Kiteworks Secure File Sharing and Governance Platform
Kiteworks’ FedRAMP and FIPS 140-2 compliant file sharing and governance platform enables public entities to share sensitive information quickly and securely while maintaining full visibility and control over their file-sharing activities. The Kiteworks platform provides:
Secure File Sharing
Kiteworks is ISO 27001, ISO 27017, and ISO 27018 certified and enables public entities to access and share personal data securely, reducing the risk of data breaches, malware attacks, and data loss.
Governance and Compliance
Kiteworks supports SDAIA National Data Governance Interim Regulation compliance and provides comprehensive reports on file activity and access.
Simplicity and Ease of Use
Kiteworks enables secure file sharing and collaboration among public entities, individuals, and third-party organizations.
Automation
Kiteworks improves operational efficiency by automating information flows and data sharing with partners and individuals to reduce manual steps and human error.
The Kiteworks Platform and SDAIA National Data Governance Interim Regulations
Section: Data Classification Interim Regulations
| SDAIA Data Classification Interim Regulations | Security Requirement Description | Kiteworks Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Principle 2: Classification Based on Necessity | Where data must be classified, the level of classification, and the safeguards and controls associated with the classification level, should be based on the potential adverse impact as a result of unauthorized disclosure, subject to the nature and sensitivity of the data. | All users are assigned a set of permissions that control access to features and resources. Kiteworks is designed so users are automatically given the least permissions necessary; administrators must explicitly enable elevated permissions. |
| Principle 3: Timely Classification | Data should be classified upon creation or upon being received from another entity and the classification exercise should be timebound. | The platform’s data classification features are integrated with its access control capabilities, allowing organizations to control who can access data based on its classification. |
| Principle 4: Highest Level of Protection | If information includes an integrated set of data with different classification levels, the highest classification level should be applied to the aggregated data. | Kiteworks’ data classification capabilities are flexible and customizable, allowing organizations to define their own classification categories and criteria. The platform provides an audit log for all data actions, including classification, ensuring that organizations have a complete record of how their data has been classified and handled. |
| Principle 5: Segregation of Duties | Duties of participants in the classification process should not overlap in terms of classifying data, approving a classification decision, granting authorization for access or usage of data, accessing data, protecting data, or disposal of data—in a way that does not lead to overlapping specialization or dissipation of liability. | Kiteworks has a separate set of admin roles that control access to administrative features. Kiteworks automatically detects unsafe configurations and warns administrative users. All users are assigned a set of permissions that control access to features and resources. Kiteworks is designed so users are automatically given the least permissions necessary; administrators must explicitly enable elevated permissions. |
| Principle 6: Need to Know | Access to data should be provided only if there is a legitimate requirement for usage of the data based on authorization and access controls and for the least number of people possible. | All users are assigned a set of permissions that control access to features and resources. Kiteworks is designed so users are automatically given the least permissions necessary; administrators must explicitly enable elevated permissions. |
| Principle 7: Least Privilege | Access to and use of data should be limited to the minimal access required to satisfy the needs of the assigned. | Kiteworks provides a specialized repository for managing users. Trusted business users can invite external users to shared folders and SFTP directories, or send them a secure email. A new external user onboards via self-service and is assigned a restricted profile (user role) with least-privilege permissions. All users are assigned a set of permissions that control access to features and resources. Kiteworks is designed so users are automatically given the least permissions necessary; administrators must explicitly enable elevated permissions. |
Section: Personal Data Protection Interim Regulations
| SDAIA Personal Data Protection Interim Regulations | Security Requirement Description | Kiteworks Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Principle 1: Accountability | Data Controller’s privacy policies and procedures shall be identified, documented, and approved by the head of entity (or his designee) and circulated to all concerned parties. | Kiteworks customers can configure legal notices that appear at sign-on describing their policies on this information. Additionally, if they don’t want to use that feature, public entities can send a file directly, and when end-users view a shared folder where they have Owner, Manager, or Collaborator privileges, they can click a Track button next to each file and folder. This will display a table showing which recipients have accessed or modified it. Users can click on any entry in this table to see its exact history of downloads, views, and other interactions. The system also converts logs to various human-readable forms for many uses. This includes administrative reporting of all activities, which is filterable and searchable. |
| Principle 3: Choice and Consent | The purpose for collection of any personally identifiable data shall be made clear to Data Subject and their (implicit/explicit) approval shall be obtained regarding collection, use, and/or disclosure of personal data before collection. | Kiteworks’ secure web forms and data collection mechanisms provide a robust solution for organizations to obtain explicit consent from users for the collection and use of their personal information, in compliance with data protection regulations. |
| Principle 4: Limiting Data Collection | Collection of any personal data shall be limited to minimum data that enables fulfillment of purposes provided for in Privacy Notice. | Kiteworks allows for customization of the branding and text on your web forms. This can include the minimum data that enables fulfillment processes. This can also include hyperlinks that can be used to direct users to additional information, terms and conditions, privacy policies, or other relevant webpages. |
| Principle 5: Use, Retention, and Destruction | Personal data usage shall be restricted to purposes provided for in Privacy Notice, which the Data Subject has implicitly or explicitly approved. Moreover, data shall be retained as long as necessary to achieve its intended purposes or as required by laws and regulations. Furthermore, data shall be destroyed in a safe manner that prevents leakage, loss, theft, misuse, or unauthorized access. | Once a deletion request is made, the information is permanently removed from the system. When personal information is deleted in Kiteworks, it is securely removed. This helps to ensure the privacy and security of user data. Kiteworks maintains a complete audit log of all user activity, including file deletions. This allows organizations to track who deleted a file, when it was deleted, and from where. This audit log can be used to support investigations and demonstrate compliance with data protection regulations. |
| Principle 6: Access to Data | Entities shall provide a means by which any Data Subject can review, update, and correct their personal data. | Kiteworks provides features that allow for the deletion of personal information collected through its web forms. Users have control over their personal information in Kiteworks. They can request the deletion of their personal information at any time. Once a deletion request is made, the information is permanently removed from the system. When personal information is deleted in Kiteworks, it is securely removed. This helps to ensure the privacy and security of user data. Kiteworks maintains a complete audit log of all user activity, including file deletions. This allows organizations to track who deleted a file, when it was deleted, and from where. This audit log can be used to support investigations and demonstrate compliance with data protection regulations. |
| Principle 7: Data Disclosure Limitation | Disclosure of personal data to third parties shall be restricted to the purposes provided for in Privacy Notice, which was approved by Data Subject. | Kiteworks provides robust security measures to protect personally identifiable information (PII) when shared with third parties. The platform’s encryption capabilities ensure that PII is protected both in transit and at rest, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Kiteworks allows for granular access controls, ensuring that only authorized third parties can access the shared PII. The platform’s audit log capabilities provide visibility into who has accessed the PII, when, and what actions they have taken, aiding in compliance with data privacy regulations. |
| Principle 8: Data Security | Personal data shall be protected from leakage, damage, loss, theft, misuse, modification, or unauthorized access – according to the controls issued by the National Cybersecurity Authority and the relevant authorities. | Kiteworks takes the protection of PII very seriously. It uses a variety of methods to ensure the security of this sensitive data, including audit logs, least access defaults, and encryption. Kiteworks maintains a complete audit log of all user activity. This includes who accessed what data, when they accessed it, and from where. These audit logs can be used to detect and investigate unauthorized access to PII. They also provide a record of data access and modification, which can be used to demonstrate compliance with data protection regulations. Kiteworks uses a least-privilege access control model. This means that by default, users are only given access to the data they need to perform their job functions. This helps to minimize the risk of unauthorized access to PII. Access controls can be managed at the individual role level, allowing for granular control over who can access what data. All data in Kiteworks, including PII, is encrypted. This includes data at rest and data in transit. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read without the encryption key. This provides an additional layer of protection for PII. |
| Principle 9: Data Quality | Personal data shall be maintained after verification of its accuracy, completeness, and timeliness, and such data shall be directly relevant to purposes provided for in Privacy Notice. | Kiteworks maintains a complete audit log of all user activity, including file deletions. This allows organizations to track who deleted a file, when it was deleted, and from where. This audit log can be used to support investigations and demonstrate compliance with data protection regulations. |
| Principle 10: Monitoring and Compliance | Compliance with Data Controller’s privacy policies and procedures shall be monitored, and any privacy-related inquiries, complaints, and disputes shall be addressed. | Kiteworks maintains a complete audit log of all user activity, including file deletions. This allows organizations to track who deleted a file, when it was deleted, and from where. This audit log can be used to support investigations and demonstrate compliance with data protection regulations. |
Section: Data Sharing Interim Regulations
| SDAIA Data Sharing Interim Regulations | Security Requirement Description | Kiteworks Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Principle 3: Authorized Access | All parties involved in Data Sharing should have the appropriate authority (security clearance might be needed based on the nature and sensitivity of the data), knowledge, and skills along with properly trained staff to handle shared data. | All users are assigned a set of permissions that control access to features and resources. Kiteworks is designed so users are automatically given the least permissions necessary; administrators must explicitly enable elevated permissions. Audit logs can be used to track the completion of training material by staff. |
| Principle 5: Collective Accountability | All parties involved in Data Sharing should be held accountable for Data Sharing decisions, for processing it according to the defined purposes, and for taking the necessary actions to ensure data quality and implementation of security controls as defined in the Data Sharing agreement and as prescribed by relevant national laws and regulations. | Kiteworks maintains detailed audit logs of all user and administrator activities within the system. These logs are accessible in the admin interface and can be exported to an external syslog server. This comprehensive record-keeping is crucial for compliance with various data privacy regulations. The audit logs record data access, file transfers, and user activities. This information can be used to demonstrate compliance with data privacy regulations that require organizations to monitor and control access to personal data. All users are assigned a set of permissions that control access to features and resources. Kiteworks is designed so users are automatically given the least permissions necessary; administrators must explicitly enable elevated permissions. |
| Principle 6: Data Security | All parties involved in Data Sharing should have an adequate set of security controls to protect and safeguard data and enable a secure environment for Data Sharing in line with relevant national laws and regulations, and in line with the National Cybersecurity Authority requirements. | Kiteworks offers robust encryption, both at rest and in transit, to secure sensitive data across all communication channels including email, file sharing, mobile, apps, web portals, SFTP, and automated workflows. It provides role-based access controls, secure collaboration tools, compliant storage, detailed activity audit logs, and a CISO dashboard with compliance reporting to protect sensitive data, enable secure collaboration, detect security incidents, and demonstrate compliance readiness. Kiteworks’ layered security capabilities allow organizations to securely share information and collaborate both internally and externally while ensuring data privacy and meeting regulatory requirements. |
| Principle 7: Ethical Data Use | All parties involved in Data Sharing should apply ethical practices throughout the Data Sharing process to ensure fairness, integrity, trust, and respect, and go beyond meeting data protection and security standards or other regulatory requirements. | Kiteworks enables granular access controls to restrict data access to only authorized users based on roles. It leverages enterprise-grade encryption for data at rest and in transit across all communication channels to prevent unauthorized access. Kiteworks provides secure, collaborative data storage along with comprehensive activity and audit logging to track data access, transfers, and modifications. These capabilities allow organizations to maintain control over sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access or breaches, enable secure collaboration, support incident investigation and forensics, and demonstrate compliance with data protection regulations. Overall, Kiteworks has robust mechanisms for data control, protection, and auditability to help organizations secure their data and meet regulatory requirements. |
Section: Open Data Interim Regulations
| SDAIA Open Data Interim Regulations | Security Requirement Description | Kiteworks Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Principle 2: Open Format and Machine-readable | Datasets should be made publicly accessible in a machine-readable format that allows automated processing. Data should be stored in widely used file formats (such as CSV, XLS, JSON, XML) that facilitate machine processing. | Kiteworks provides a comprehensive, immutable audit log feed that records all activities across the platform. This includes actions taken by both users and administrators, ensuring a complete record of all interactions with the system. The audit logs are unified across all communication channels and system services. This means that regardless of how an action is performed (e.g., via the web interface, mobile app, or through an integrated service like Microsoft Office or Google Workspace), it will be recorded in the audit log. The audit logs are standardized and cleaned, ensuring consistency and readability. This makes it easier for administrators to review the logs and identify any unusual or suspicious activities. Kiteworks also provides the ability to export these logs. This allows organizations to import the logs into their security information and event management (SIEM) systems, such as IBM QRadar or FireEye Helix, for further analysis and correlation with other security data. Additionally, a Splunk App using its native Splunk Forwarder is provided. This allows organizations to leverage the powerful data analysis capabilities of Splunk to gain insights from their audit logs. |